Abraham Lincoln |
Birth: 12 February 1809 |
| Died: 15 April 1865 | |
| Party: Republican | |
| Presidency: 1861 – 1865 | |
| Vice President: Hannibal Hamlin, Andrew Johnson | |
| Nickname: Honest Abe |
● Significance of Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln’s presidency was significant as he preserved the United States of America as a whole despite the Civil War.
The United States of America has expanded at an exponential rate. Incorporation of different people from different regions along with the immigrants from foreign countries into one nation was crucial for the United States of America.

Abraham Lincoln not only preserved all the states as one union, but also established the moral nationalism of the United States of America.
Although the admission of African-American as citizens and the grant of human rights took a substantial amount of time, Abraham Lincoln established a shared moral foundation for the people of the United States of America.

● Homestead Act
Over the time as the United States of America expanded, the government would sell territory to people to support their financial foundations.
However, the demand of homesteading increased, because although the United States of America vastly expanded to the west, it took extensive finances to build infrastructure and settle down on the no-man’s lands.


Homesteading meant that the government provide the land for free in exchange of a promise to cultivate and develop the provided lands.
Abraham Lincoln approved the Homestead Act that granted 160 acres of governmental territory which is about 0.65 km² for free for those who shall cultivate the land for at least 5 years.
For the next 40 years, 80 million acres which is about 324,000 km² were claimed by the Homestead Act.

● The Attack on Fort Sumter
Pierre Gustave Toutant-Beauregard (Also known as P.G.T Beauregard) mobilizes Confederate troops to attack Fort Sumter on the 12th April 1861.
Major Robert Anderson and federal troops stationed in Fort Sumter which was located in Charleston South Carolina.
South Carolina already seceded from the United States of America and Fort Sumter was a threat for Confederate States to use the Charleston harbor.


Before the attack on For Sumter, the Confederate authorities were informed by the federal government that they intended to resupply foods for the federal troops stationed in Fort Sumter. Although there were active talks, Jefferson Davis orders P.G.T. Beauregard to take over Fort Sumter before it was resupplied.
The Confederate troops bombarded Fort Sumter for about 34 hours on the 12th April 1861. Major Robert Anderson waited until the bombardment stopped and surrendered the fortress while he led the federal troops along with the U.S. flag with him north.


There weren’t any casualties during the bombardment and the counter-attacks. However, Abraham Lincoln responded to the attack of Fort Sumter by raising call for troops (initially, he tried to mobilize 75,000 troops which were raised in a remarkably short amount of time) and he ordered the navy to form a blockade on the South.


After Abraham Lincoln mobilizes more troops, an addition of 4 states including Arkansas, North Carolina, Virginia and Tennessee secedes from the Union as they justified it was inevitable due to the threat of the federal government mobilizing troops against the states.


As Virginia seceded, ironically, Lincoln initially offered Robert E. Lee the commander of the Union Army by Winfield Scott’s advice but Robert E. Lee refused by the secession of Virginia in which Robert E. Lee would later become the commander of army of the Confederate States of America
● Jefferson Davis and the Confederate States of America
Jefferson Davis was elected the first and only president of the Confederate States of America due to his political experience as a representative and a senator for Mississippi, Secretary of War and his military experience in the American-Mexican War as well.
The Confederate States made Richmond; Virginia after Virginia joins the Confederate States. The capital. Richmond was very close Washington D.C. and both capitals were close to the borders and the Mason Dixon Line which led to the intense Western campaigns during the early phases of the Civil War.


J
efferson Davis established the first cabinet for the Confederate States of America by choosing one member per state from the initial seven states Alabama, Florida, Mississippi, Louisiana, Georgia, South Carolina, and Texas.
He appointed Robert Toombs of Georgia the Secretary of State, Christopher Memminger of South Carolina the Secretary of the Treasury, LeRoy Walker of Alabama the Secretary of War, John Reagan of Texas for Postmaster General, Judah P. Benjamin of Louisiana the Attorney General, and Stephen Mallory of Florida the Secretary of the Navy.

Later on, after the attack of Fort Sumter, four more states including Arkansas, North Carolina, Tennessee, and Virginia joined. However, the government of the Confederate States of America weren’t stable enough that members of the cabinet were frequently replaced.
Also, most of the states put the state government and states’ rights first as this was one of the main reasons they’ve seceded from the Union.
Thus, Jefferson Davis’s central government had to struggle making decisions as it lacked central power.
Jefferson Davis had to struggle with the poor economy by the naval blockade, starvation and the losing war. His government would even have to pass the unconditional execution of captured African-Americans after Abraham Lincoln announced the Emancipation Proclamation.

The Confederate States also put effort on receiving support by France and Great Britain as it would be politically advantageous for European countries to split the United States apart and cotton trades with the Confederate States was essential.
However, Great Britain would solve their cotton issue by increasing cotton plantations in Egypt and other colonies and the Emancipation Proclamation and the Gettysburg Address by Abraham Lincoln granted the political justification of the Union’s cause to abolish slavery.


Both Great Britain and France favored the aristocratic Confederate States and splitting the United States, however both countries relied on food exports from the North, able to resolve cotton supplies within their colonies and the political justification to abolish slavery was so solid.
Both countries did agree on the abolition of slavery which eventually became the main cause for not standing side with the Confederacy

● Anaconda Plan
Abraham Lincoln appoints the experienced general Winfield Scott as the General-in-Chief of the United States military forces during the early phases of the Civil War.
Winfield Scott had experience during the 1812 War, Black Hawk War, and the American-Mexican War and he was a politician who was once a runner-up for presidency.
Winfield Scott intrinsically knew the close relationship between politics and war. He proposed the main strategy of the Union the Anaconda Plan which was also known as the ‘Great Snake’ to Abraham Lincoln to minimize the lives of troops.


The Anaconda Plan proposed by Winfield Scott attempted to
1. Split the Confederate Union into half by the Mississippi River and control transportation and food supplies
2. Form a naval blockade on the coast to prevent exports and imports of the Confederate States and prepare for Great Britain and France intervention.
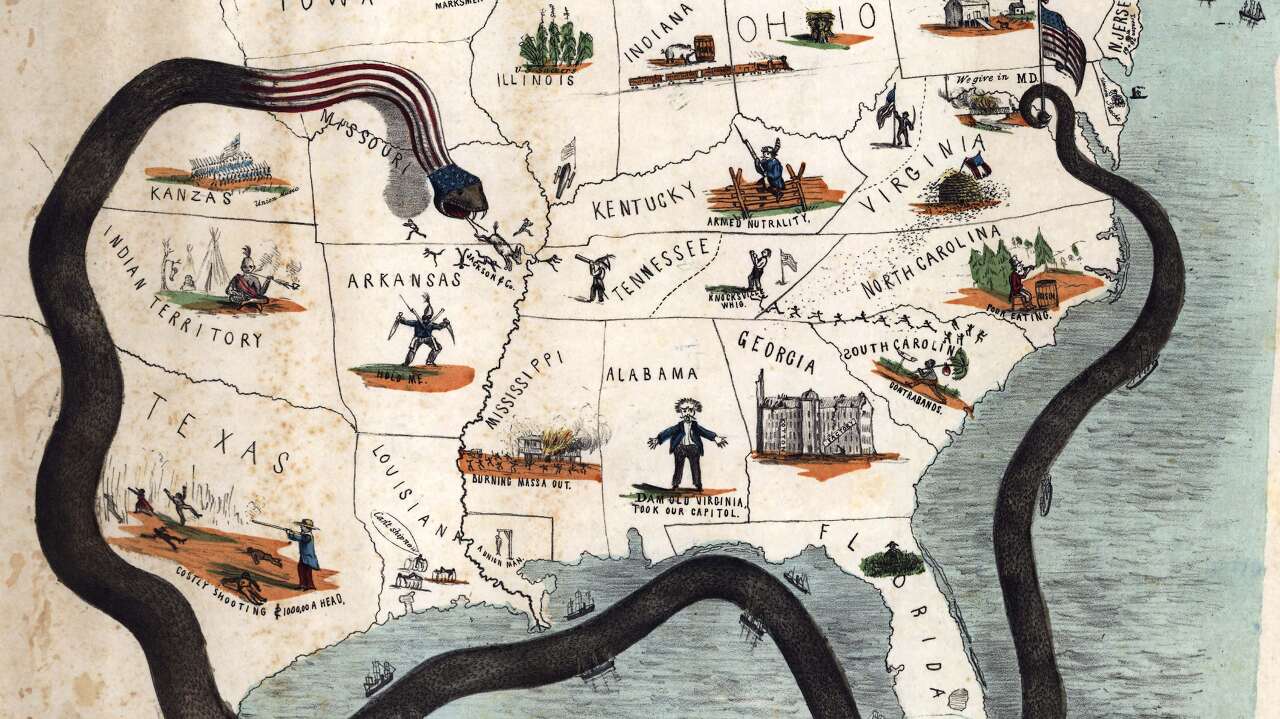
Winfield Scott already knew that it would take time for the Anaconda Plan but believed it will minimize casualties. Cotton export was crucial for the economy of the Confederate States and the south lacked manufacturing infrastructure so import of manufactured goods were crucial for the economy as well.


Also, the federal government was aware of the diplomatic attempts by the Confederacy with Great Britain and France.
Although the public didn’t support the Anaconda Plan as it was exhausting and it seemed very easy to takeover Richmond which was the capital of the Confederacy as it was close to the border.
However, the early battles of the Civil War proved the advance to Richmond wasn’t easy as it seemed. The Anaconda Plan was executed as served as a masterplan for the Union’s strategy during the Civil War.

● The first Battle of Bull Run & the Peninsula Campaign
Volunteers would rush to both the Union and the Confederacy. Even for the North, only white men were allowed to enlist which men joyfully joined singing ‘We are Coming, Father Abraham’.
However eventually, the Union would accept African-Americans to the military as well as the situations became dire. Both men from the north and south of the Mason and Dixon Line were eager for the war without realizing how brutal it shall become.


The first major engagement of the Civil war was the Battle of Bull Run.
On a creek located in the north east side of Virginia, Irvin McDowell of the Union led the Army of Northeastern Virginia against P. G. T. Beauregard’s Army of the Potomac(Don’t confuse this with the Army of the Potomac of the Union, this Confederacy is renamed after the Bull Run battle) and Joseph E. Johnston’s Army of the Shenandoah.
By this time nobody knew that the Civil War would be so brutal. People would gather to see the battle between the forces.
While both sides were inexperienced, Thomas Jackson who led the 1st Brigade of the Army of Shenandoah led the decisive charge that neutralized the artillery and lines of the Union.


After the first battle of Bull Run, Lincoln reforms the major Union forces in the east. The Union army was reassembled as the Army of the Potomac. Lincoln puts George B. McClellan as the commanding officer of the Army of the Potomac.
After a series of changes in command, Jefferson Davis names Robert E. Lee command of the Army of Northern Virginia which became the main force in the east for the Confederate States.


George B McClellan’s Army of the Potomac sailed from Alexandria and landed on Fort Monroe, Virginia in the spring of 1862. George McClellan’s strategic objective was to capture Richmond which was the capital of the Confederate States and end the war as soon as possible
. Although the Anaconda Plan was in effect, Abraham Lincoln was pressured by the public to end the war as soon as possible. These series of battles were referred as the Peninsular Campaign.


The Army of the Potomac were able push their way through along the Chickahominy River to a point where they were just miles away from Richmond.
However. the Union failed to break the Confederate Stats’s defense lines during the Battle of Seven Pines (also referred as Battle of Fair Oak Station) and the Seven Days Battles.
Although the Confederate States had more casualties, George B McClellan’s cautious nature allowed multiple counter attacks and failed to make a decisive blow in the defensive lines of Richmond.
Lincoln eventually orders the Army of the Potomac to retreat and support the newly formed Army of Virginia under John Pope’s command for the Northern Virginia Campaign.

● Northern Virginia Campaign and the Battle of Antietam
John Pope had close relations with Lincoln and he took command of the Army of Virginia and became the main force for the Northern Virginia Campaign.
The Army of Virginia’s key objectives were defending Washington D.C. (confront the Confederacy forces) while pressurizing the public in the Confederate States, and lure Confederate forces from the Virginia peninsula so the Army of the Potomac could advance to Richmond.


However, the Robert E. Lee’s Army of Northern Virginia was able to successfully divide joint operations between the Army of Virginia and the Army of the Potomac by maneuvering tactics by the Second Battle of Bull Run(Also referred as the Battle of Manassas)
The Army of Virginia was dissolved with only forces enough to defend Washington D.C. while the Army of Potomac would need time to reform.

John Pope was relieved from command which would have been a more severe punishment if it wasn’t for his friendship with Lincoln. Robert E. Lee leads the Army of Virginia across the Potomac River as the Army of Virginia confronting was dismissed.
Robert E. Lee thought it was a great opportunity to counter attack and invade Maryland which is also referred as the Maryland Campaign.

Robert E. Lee attempted to cut the B-O line(Baltimore-Ohio Railroad line) that supplied Washington D.C. and attempted to directly threaten the federal capital.
However, the Confederate States were poorly supplied in munitions and men and the Army of North Virginia only had approximately 55,000 men in force which recued to 45,000 men just in 10 days due to desertion, starvation and lack of supplies.



Robert E. Lee and the Confederate forces saw limited victory in Harpers Ferry. However, George McClellan and the Army of the Potomac which was about 100,000 in size were on the verge of ‘Divide and Conquer’ by pursuing on the split Confederate forces.
However Robert Lee gets enough time to unite his forces during the Battle of South Mountain. George McClellan and the Army of the Potomac and Robert E. Lee and the Army of Northern Virginia confront each at Antietam Creek which was close to Sharpsburg.

The Battle of Antietam became one of the bloodiest day in American history. During the Battle of Antietam that was only a single day in 16th, September 1862, 20,000 men were killed.
The casualties between both sides were similar but Robert E. Lee would have to retreat from Maryland across the Potomac River. Lincoln replaced McClellan with Ambrose Burnside disappointed with McClellan failing to pursuit Robert Lee’s retreat.


● Emancipation Proclamation – Proclamation 95
Abraham Lincoln issued the Emancipation Proclamation on the 22nd September 1862. He attempted to issue the Emancipation Proclamation anticipating victory from the Battle of Antietam which did fail.
The Emancipation Proclamation was to take effect on 1st January 1863.

Lincoln announced ‘That all persons held as un-free men within the rebellious states are and henceforward shall be free’.
The Emancipation Proclamation applied to the 10 states that seceded from the United States(Tennessee was under Union control, so it wasn’t applied) which did exclude the slavery states that stayed with the Union.

However, the Emancipation Proclamation justified the Civil War as a war for freedom rather than a war to preserve the Union. It also allowed African-Americans to join the military and fight for their own freedom.
European nations such as Great Britain and France that saw the Civil War as an opportunity to split the power of the United States also lost cause in any means to support the Confederate States as the Civil War developed to a war to achieve justice and abolish slavery.


'International & History' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [USA] - 미국 11대 대통령 제임스 녹스 폴크 (0) | 2023.03.07 |
|---|---|
| [USA] - 16th President of the USA Abraham Lincoln feat. American Civil War - Part 2 (0) | 2023.03.07 |
| [USA] - 미국 9대 대통령 윌리엄 헨리 해리슨 미국 10대 대통령 존 타일러 (0) | 2023.03.07 |
| [USA] - 15th President of the USA James Buchanan (0) | 2023.03.07 |
| [USA] - 미국 8대 대통령 마틴 반 뷰렌 (0) | 2023.03.07 |



