Abraham Lincoln |
Birth: 12 February 1809 |
| Died: 15 April 1865 | |
| Party: Republican | |
| Presidency: 1861 – 1865 | |
| Vice President: Hannibal Hamlin, Andrew Johnson | |
| Nickname: Honest Abe |
● The Battle of Fredericksburg
Lincoln orders Ulysses S. Grant and the Army of the Tennessee to march through the west of the Confederate States to take control of the Mississippi River while he orders Ambrose E. Burnside another plan to capture Richmond.
Ambrose E. Burnside establishes a plan to capture Richmond and end the war upon Washington’s pressure. He intends to cross the Sothern Rappahannock River and take control of the Fredericksburg and Potomac Railroad (RF&P) that could lead straight to Richmond before Robert E. Lee’s forces could catch up.
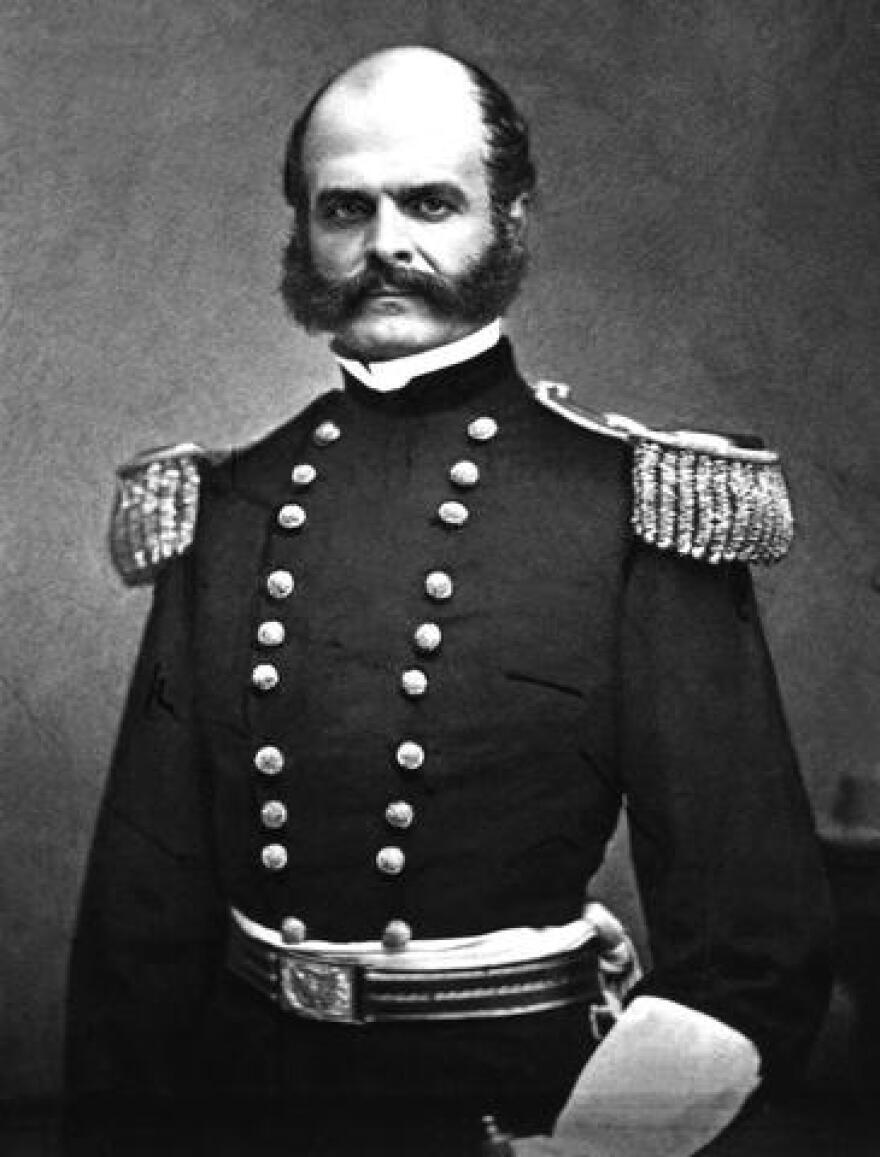

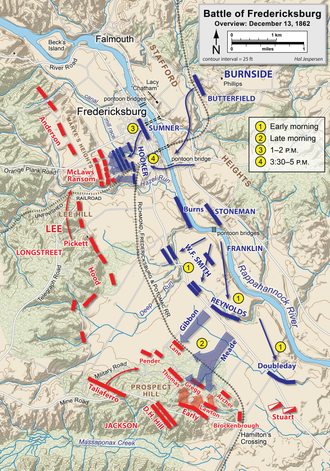
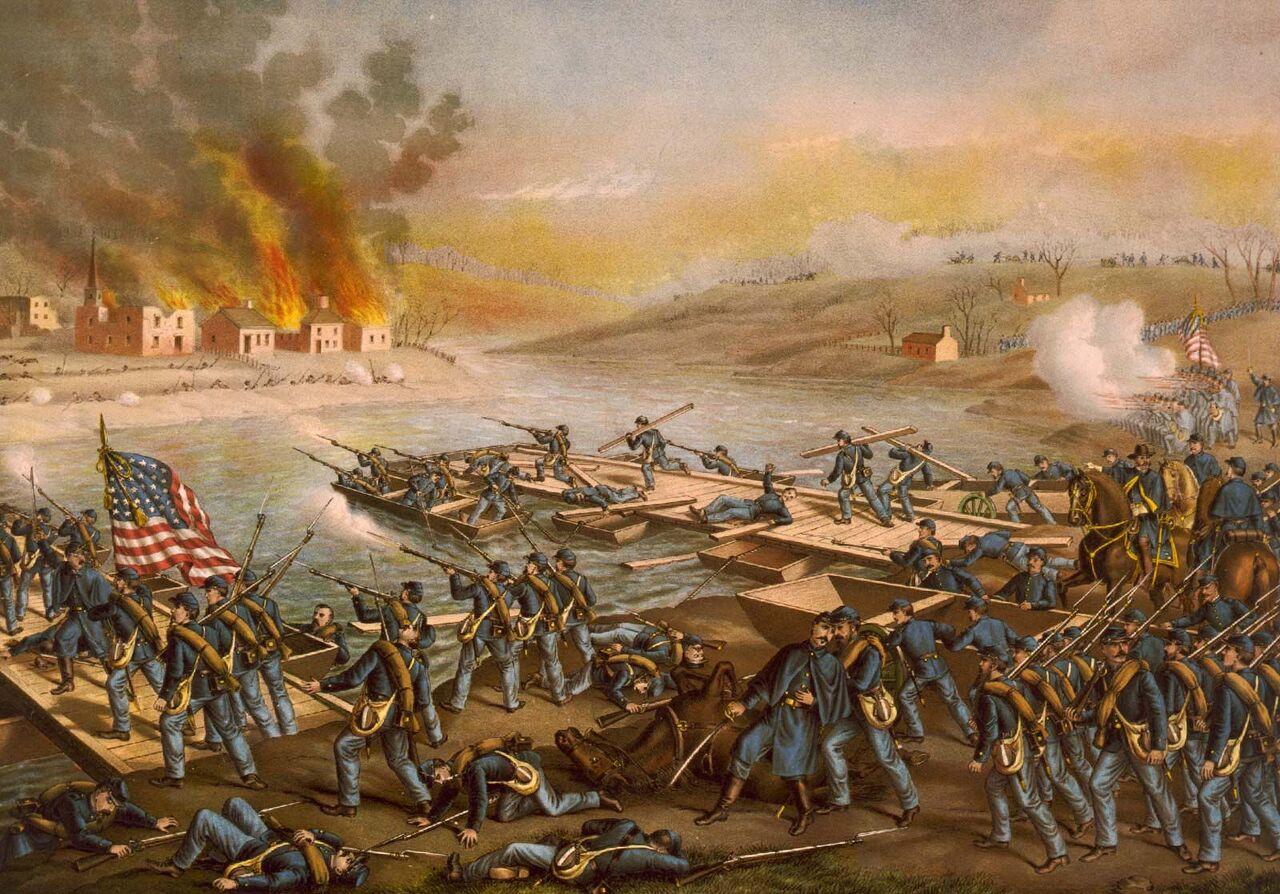
Ambrose E. Burnside and the 120,000 troops of the Army of the Potomac arrive at the Rappahannock River in December 1862.
After the Union forces occupies Fredericksburg after substantial sacrifice crossing the river and urban combat, Burnside decides to attack the entrenched Confederate forces.


However, the Confederate forces under James Longstreet’s command slaughtered Union troops.
The Army of the Potomac would have to retreat after suffering 12,000 casualties compared with the 6,000 casualties on the Confederate side.
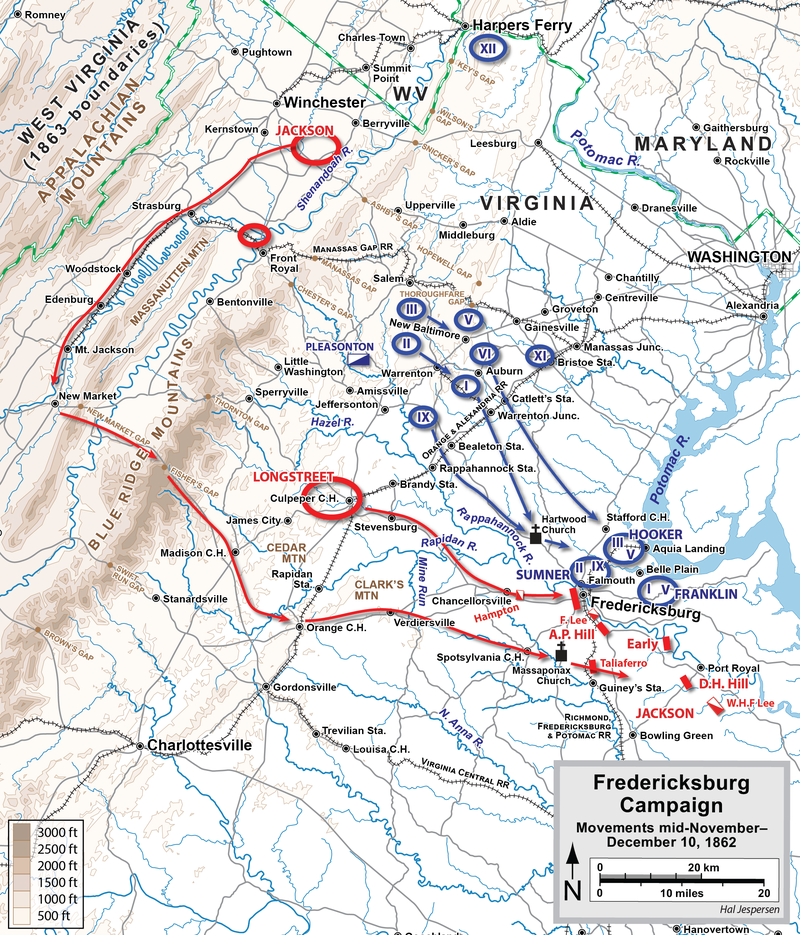
The retreat of the Army of the Potomac was referred as the ‘Mud March’ and Ambrose would resign his position. Abraham Lincoln appoints Joseph Hooker the new commander of the Army of the Potomac.
By this time, rather than attempting to capture Richmond at once, the strategic focus became the annihilation of the Northern Army of Virginia.


● The Battle of Chancellorsville
Joseph Hooker proposes the ‘Perfect Plan’ that intended to circle Robert Lee and the Northern Army of Virginia in Fredericksburg.
Joseph Hooker would mobilize troops to the west of the Rappahannock River while utilize the cavalry to detour far west to intervene between the Northern Army of Virginia and Richmond.
On April 27th 3 corps of the Army of the Potomac moved west along the Rappahannock River and Rapidan River and crossed the river and rendezvous on Chancellorsville.

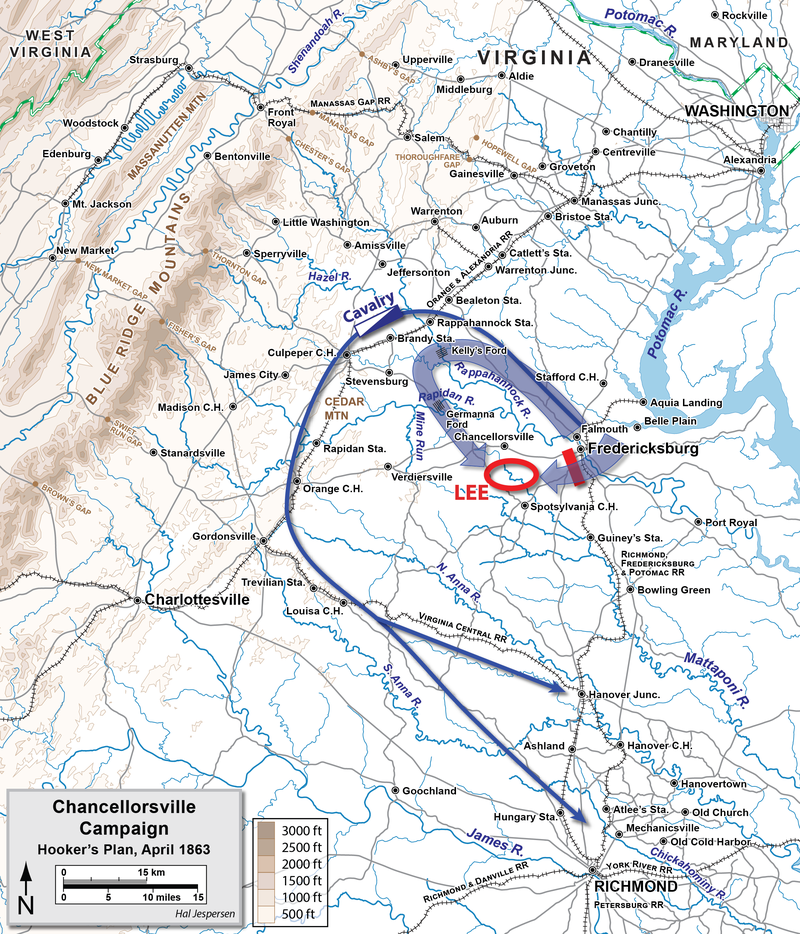
By 1st of May, about 70.000 troops from the Army of the Potomac rallied in Chancellorsville.
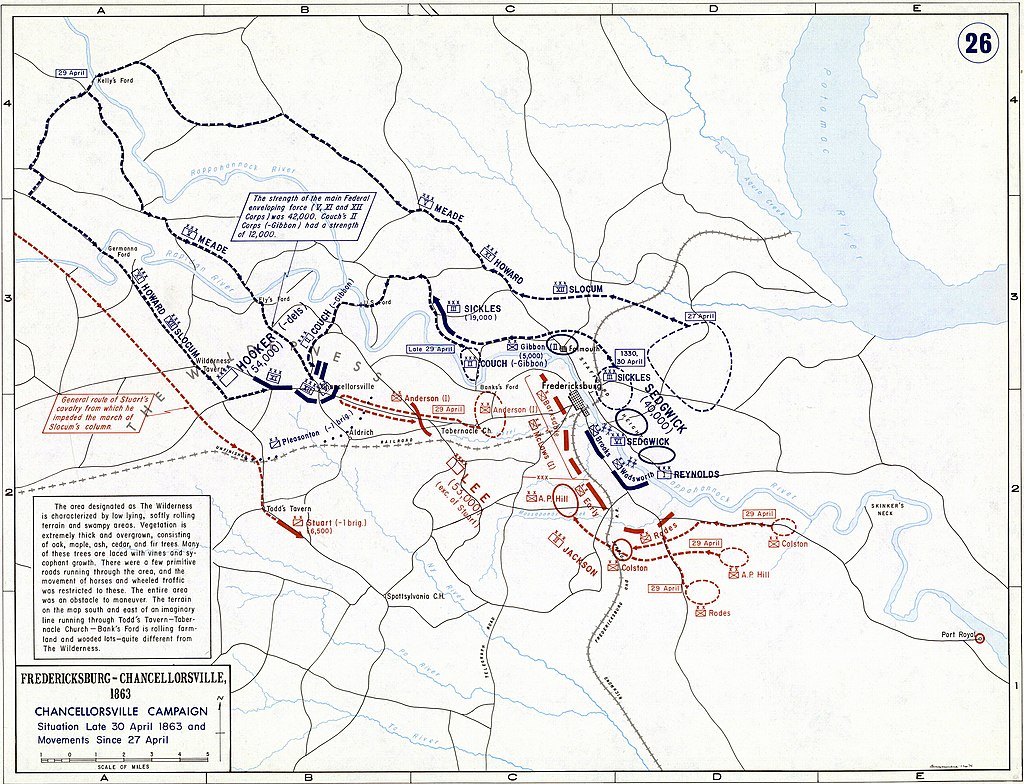
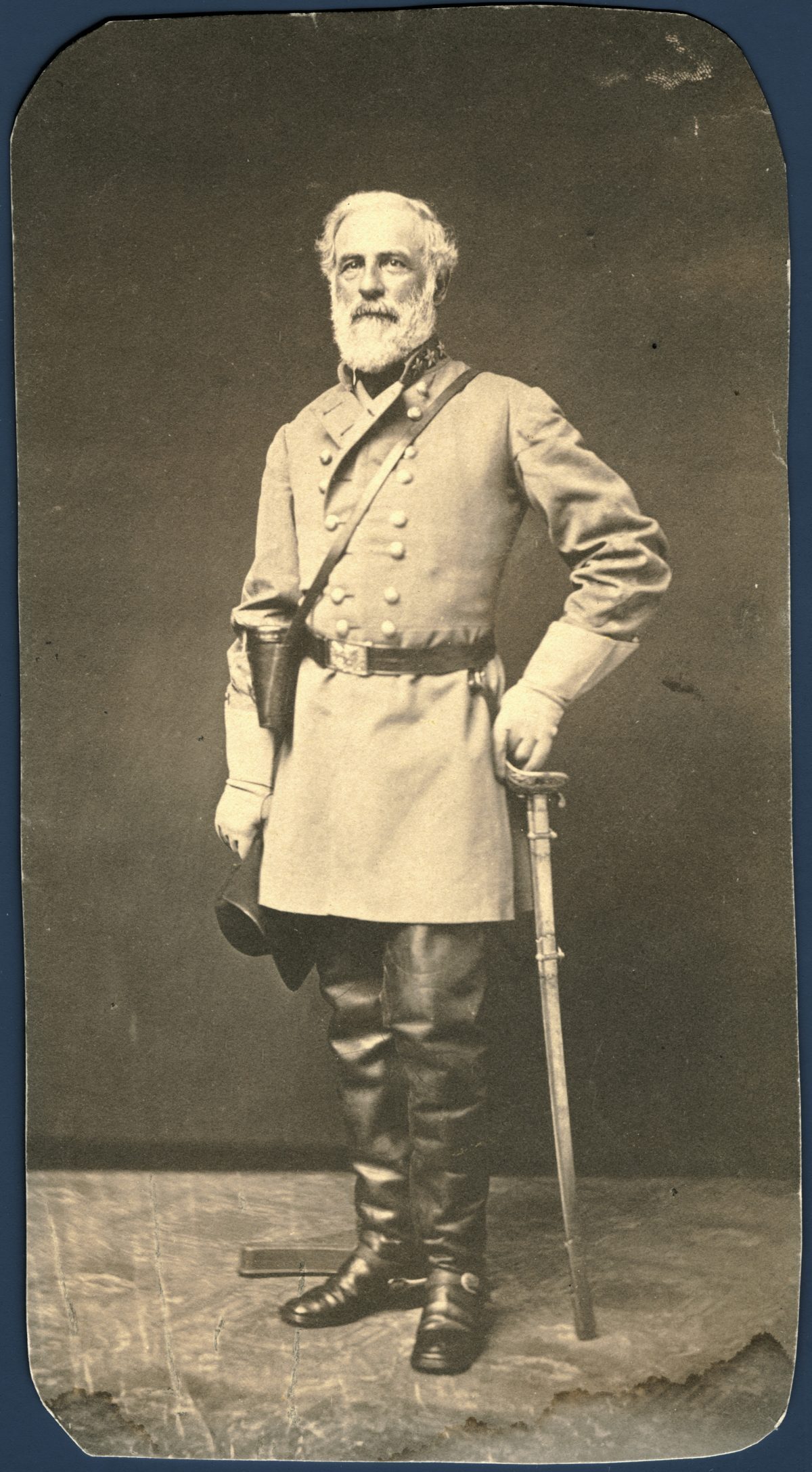
Robert E. Lee would make a rather odd position and decide to leave about 10,000 men in Fredericksburg which John Sedgwick’s 40,000 Union troops were confronting.
Robert E. Lee took the rest of the Northern Army of Virginia to confront the Union troops in Chancellorsville on 1st of May 1863.

On the 2nd of May, Robert E. Lee divides his forces once again. He gives Thomas ‘Stonewall’ Jackson orders to maneuver west and attack the west flanks of the Union army.
Despite the bold offensives by the Confederates, the Union army outnumbered the Confederate forces and established a good defensive line.
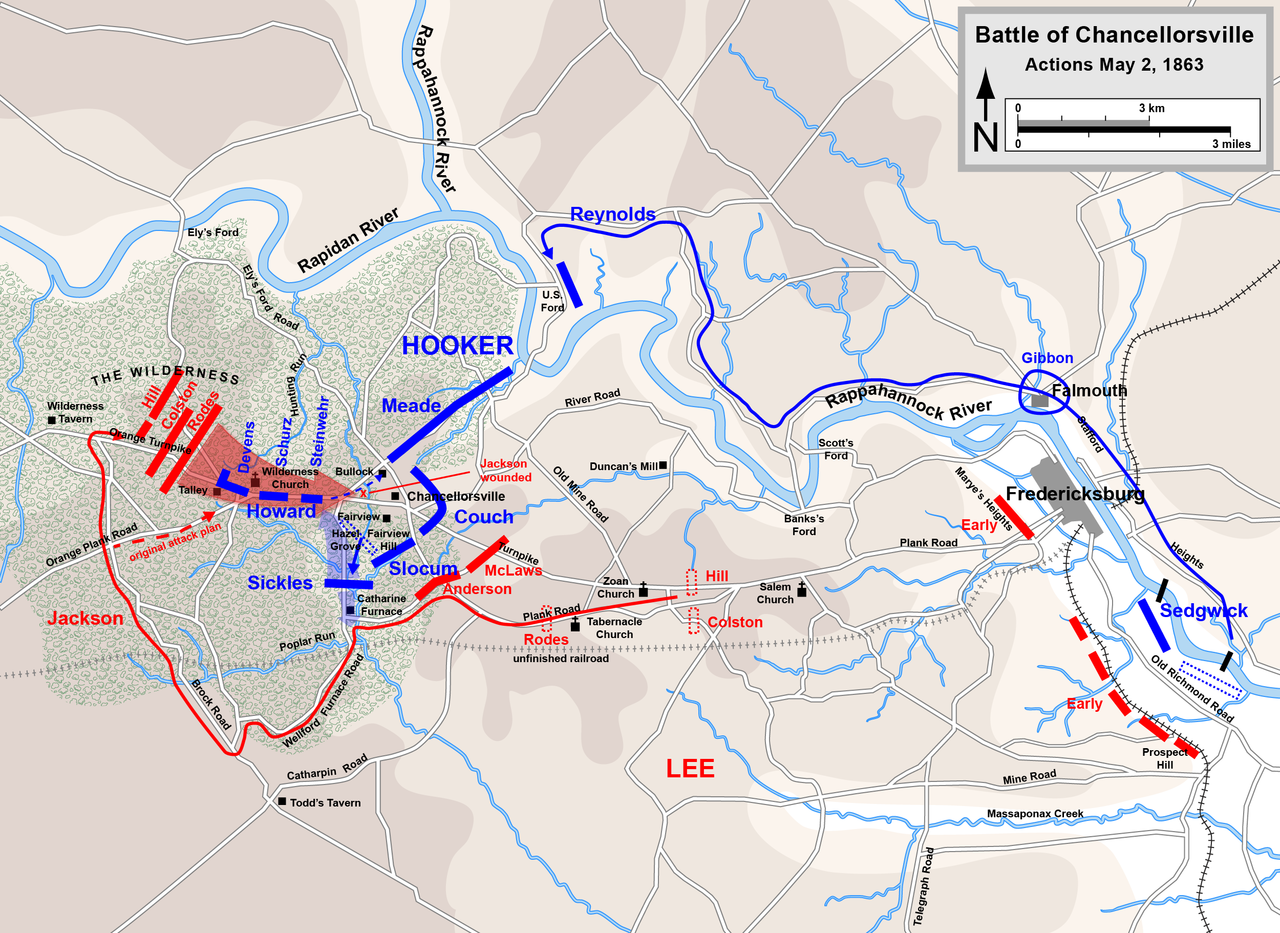
On the 3rd of May, John Sedgwick’s Union forces broke through the Confederate lines at Fredericksburg and attempted to march to Chancellorsville.
The battles between the Confederate troops and the Union troops around Fredericksburg included the Second Battel of Fredericksburg and the Battle of Salem Church.
These battles cost 20,000 lives which was the second bloodiest day ranking behind the Battle of Antietam.

Both battle fronts near Chancellorsville and Fredericksburg stalled into a ceasefire. Joseph Hooker already failed his strategic objectives trying to rapidly encircle the Army of Northern Virginia.
Although the generals of the Union insisted on keeping the fight, Joseph Hooker decides to retreat.

Lincoln would quote "My God! My God! What will the country say?" upon the defeat at Chancellorsville and later relieve Hooker and appoint George Meade in command of the Army of the Potomac just before the Battle of Gettysburg.
The public was shocked as well as the more well equipped, well supplied Union army that even outnumbered the Confederates kept losing.
However, the Confederate States have also constantly suffered casualties. Already, the economy of the Confederate States worsened and it lacked the infrastructure and supplies that the North had. Also, Robert E. Lee’s most reliable commander Stonewall Jackson died who was unable to recover the wounds from friendly-fire.

● The Battle of Gettysburg
Robert E. Lee leads another invasion north to Pennsylvania that was called the Gettysburg Campaign in June 1863.
The Confederate States government wanted to support the Vicksburg stronghold in Mississippi, however Robert E. Lee insisted on the invasion North. Robert E. Lee believed that his forces would threaten Washington D.C. and encourage the public’s demand for a peace treaty while seizing supplies as Virginia was scorched by the constant battles.


Considering the fact that Ulysses S. Grant and his Army of the Tennessee seized the Confederate Army of Mississippi led by John C. Pemberton from May to July, either strategic choice between reinforcing Confederate forces in the west or march to Pennsylvania would have failed.
(John C Pemberton’s confederate forces officially surrender in 4th July 1863 and the Union has full control of Vicksburg and the Mississippi River.)


On June 3rd, about 75,000 men of the Northern Army of Virginia moved west from Fredericksburg, intended to head to Pennsylvania through West Virginia. Joseph Hooker’s Army of the Potomac would chase the Confederate troops north.


As the Confederate troops rushed north with the Union forces chasing them, there were several battles including the Battle at Brandy Station, Winchester, Aldie, Middleburg, Upperville, Hanover, Carlisle, and Hunterstown.
After these battles on June 27th, Lincoln relieves Hooker and appoints George Meade the commander of the Army of the Potomac.

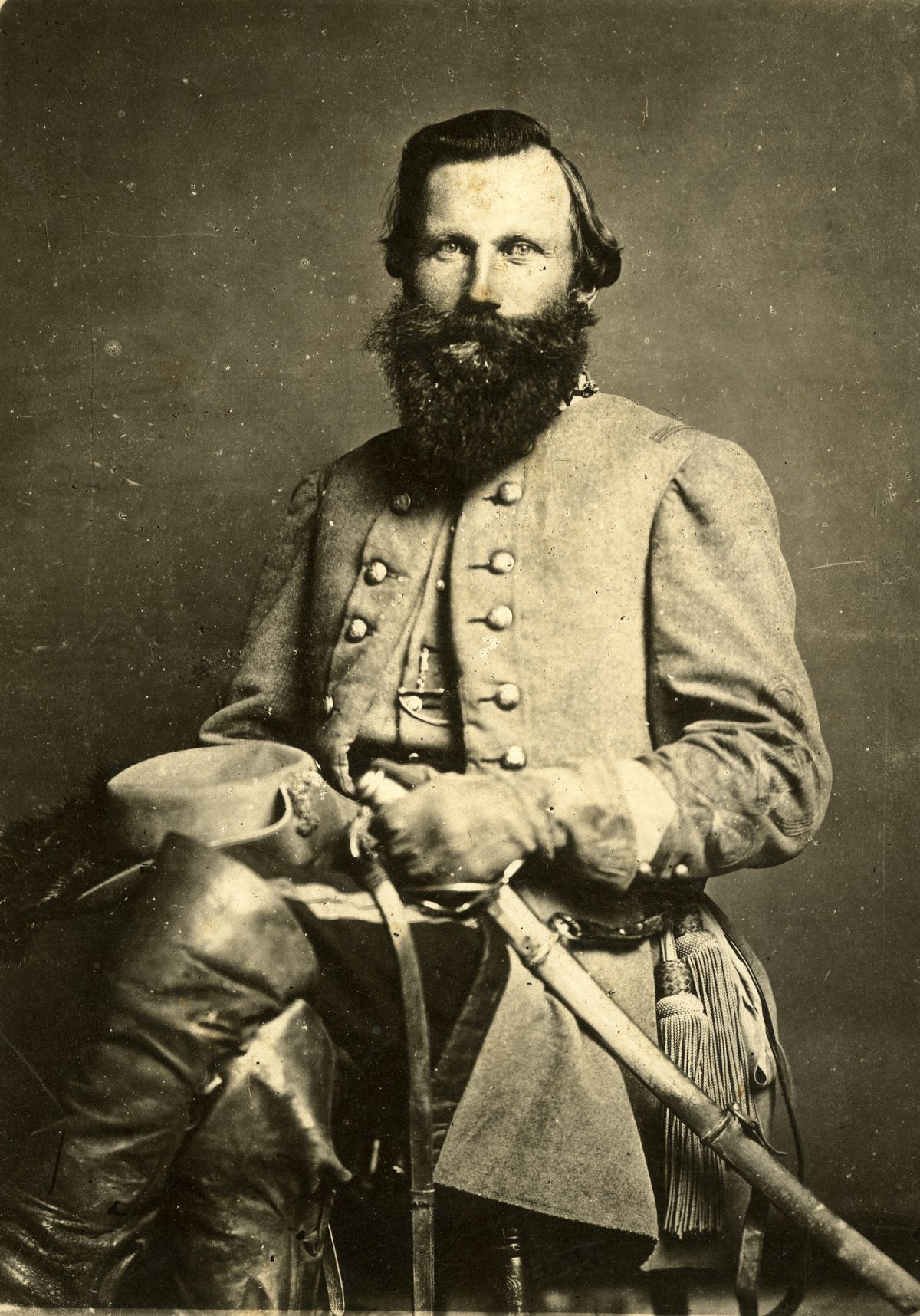
The Confederate troops massed the cavalry under command of James Ewell Brown "Jeb" Stuart who was supposed to provide reconnaissance, intel and protect the flanks of the Confederate troops.
However, Jeb Stuart failed to provide such intelligence to Robert E. Lee and left the Confederate forces unattended.


Robert E. Lee didn’t expect the Army of the Potomac to follow the marching speed of the Confederate forces but on 29th June, he finds out that the Army of the Potomac was closing in and already cut off the Confederate force’s route to Virginia.
Robert E. Lee finds this intel by a spy hired by James Long Street named Henry Thomas Harrison and still Jeb Stuart was absent.


Robert E. Lee orders his forces to concentrate at the outskirts north of Gettysburg. The Confederate troops pushed the Union south of Gettysburg despite efforts by John Buford’s cavalry and John F. Reynold’s 1st Corps.
However, the Army of the Potomac were able to mass in a god defensive position in ‘Cemetery Ridge’. ‘Little Round Top’ and the ‘Devil’s Den’ on 1st July thanks to the efforts of John Buford and John F. Reynolds (Reynolds was unfortunately killed in action by a sniper)
However, the Confederate forces failed to take the high ground due to miscommunications while the Union forces clustered.
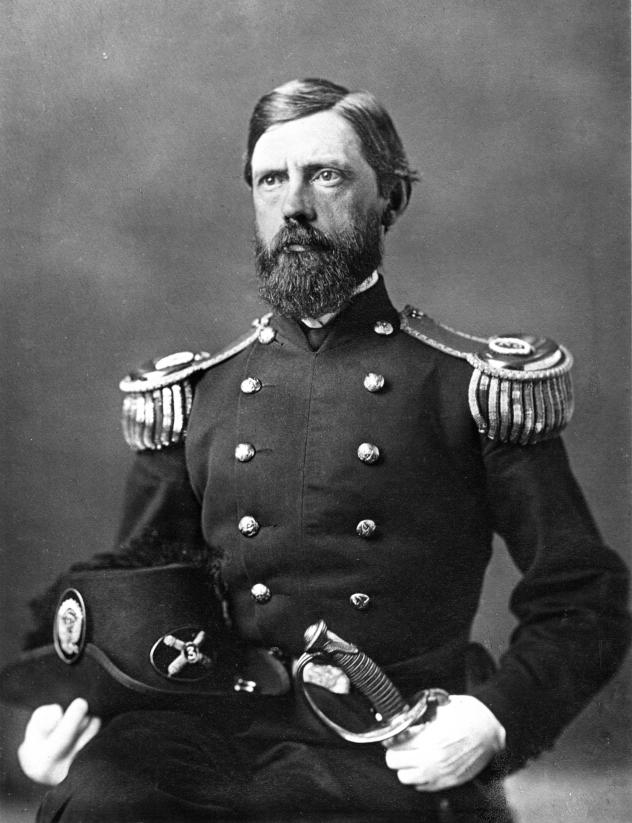
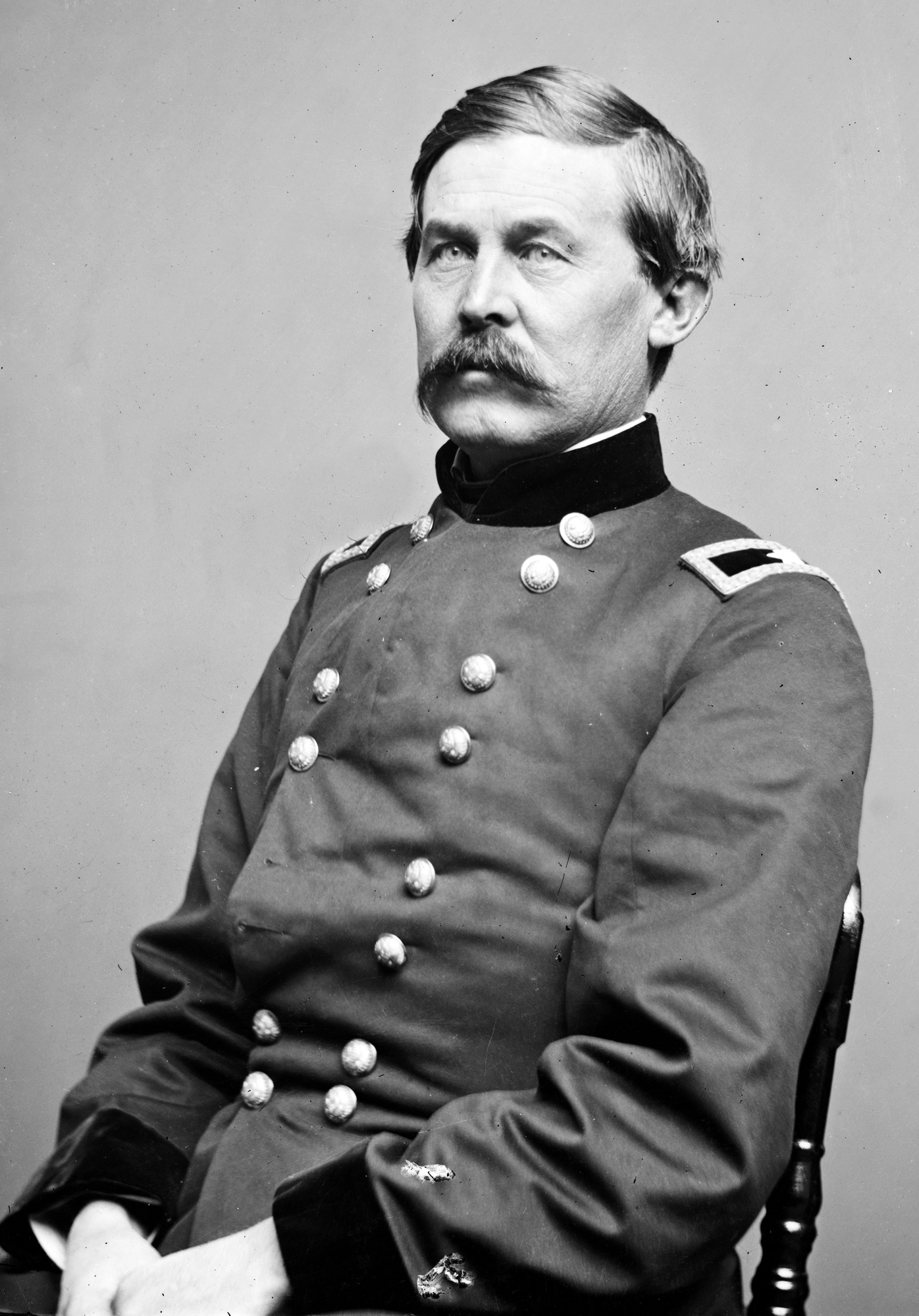


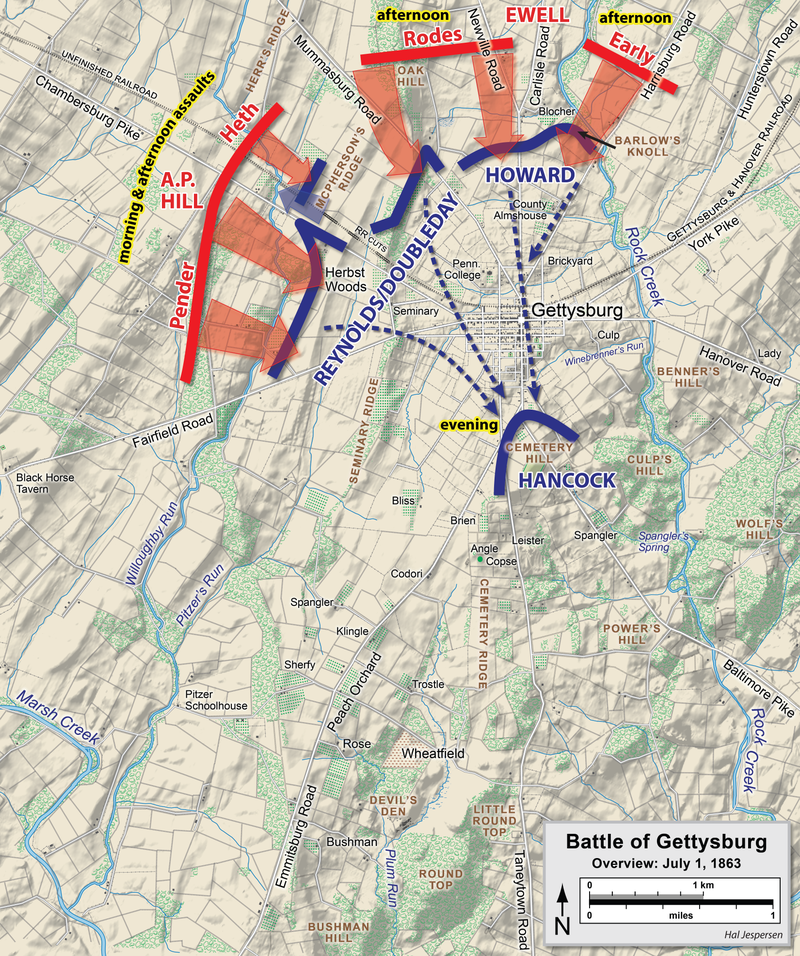
On the 2nd of July, Robert E. Lee attacks the flanks of the Union army.
However, the union army was well entrenched in the high ground and the Confederate Army was only able to push the forces on the southern west flank a little bit further.
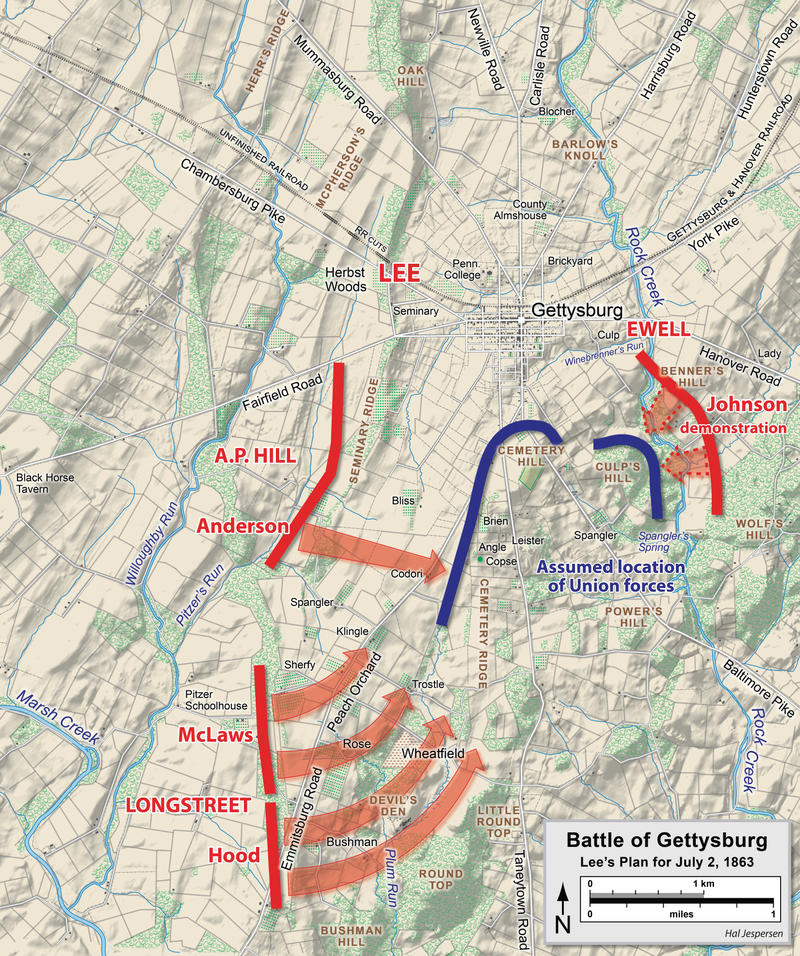
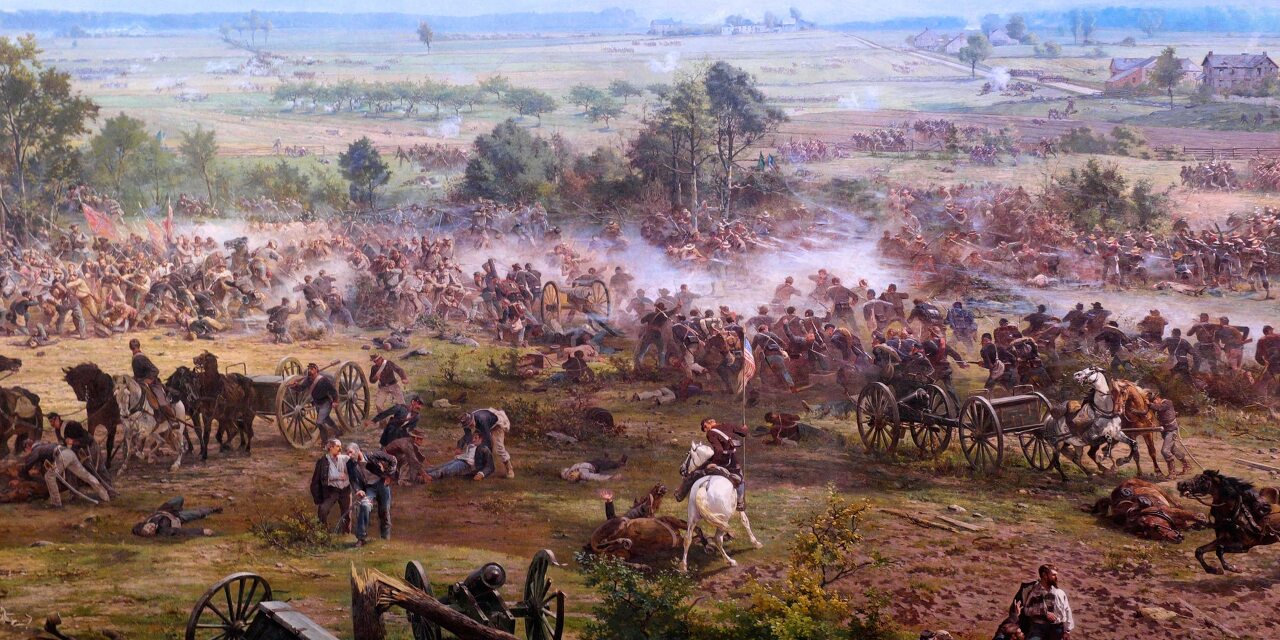
On the 3rd of July, Robert E. Lee orders an attack on the center of the Union forces believing that the Union forces would have redeployed their forces on the flank.
This would lead to the infamous Pickett’s Charge (Pickett–Pettigrew–Trimble Charge).
Even though the Confederate forces concentrated all artillery on the center, the charge of George Pickett’s division(along with Pettigrew and Trimble) led to a massacre. About 1,000 men were killed 4,000 wounded and 4,000 captured by the Pickett’s Charge alone.

On 4th of July, Robert E. Lee decides to retreat back to Virginia as his overwhelmed troops.
The Army of Northern Virginia suffered 27,000 casualties but this was critical as the Confederate States had a much smaller population.
This along with the surrender of Vicksburg on July 4th became the decisive blow for the Confederate States.


● The Gettysburg Address
Abraham Lincoln travels to Gettysburg to dedicate the lives at Gettysburg on 19th November 1863.
Abraham delivers a speech later called the Gettysburg Address which justified the cause of the Civil War with only 272 words without even mentioning the battle or slavery.
Perhaps the most famous phrase of the Gettysburg Address that would inspire people for an eternity shall be the idiom of democracy “Government of the people, by the people for the people”

The Gettysburg Address became one of the most important speeches in the history of the United States. The Gettysburg Address also solidified the cause of the Civil War along with the Emancipation Proclamation.
The Gettysburg Address
Four score and seven years(one score equals 20 years) ago our fathers brought forth on this continent, a new nation, conceived in Liberty, and dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal.
Now we are engaged in a great civil war, testing whether that nation, or any nation so conceived and so dedicated, can long endure.
We are met on a great battle-field of that war.
We have come to dedicate a portion of that field, as a final resting place for those who here gave their lives that that nation might live. It is altogether fitting and proper that we should do this.
But, in a larger sense, we can not dedicate—we can not consecrate—we can not hallow—this ground.
The brave men, living and dead, who struggled here, have consecrated it, far above our poor power to add or detract.
The world will little note, nor long remember what we say here, but it can never forget what they did here.
It is for us the living, rather, to be dedicated here to the unfinished work which they who fought here have thus far so nobly advanced.
It is rather for us to be here dedicated to the great task remaining before us—that from these honored dead we take increased devotion to that cause for which they gave the last full measure of devotion—
that we here highly resolve that these dead shall not have died in vain—that this nation, under God, shall have a new birth of freedom— and that government of the people, by the people, for the people, shall not perish from the earth.



● Siege of Vicksburg & Sherman’s March to the Sea
Lincoln ordered Ambrose Burnside to capture Richmond when Burnside was commander of the Army of the Potomac in December of 1862. Meanwhile Lincoln also ordered Ulysses S. Grant and the Army of the Tennessee to capture Vicksburg.

Vicksburg was probably the most important strategic point during the whole Civil War.
It was one of the connecting points of the Southern Railroad of Mississippi and the Vicksburg, Shreveport & Texas Railroad which connected the Confederate States and supported the economy of the Confederate States.
It was also a natural fortress which was hard to capture.
The Union navy already seized the south of the Mississippi River but the Union navy could not control the Mississippi River because of Vicksburg.

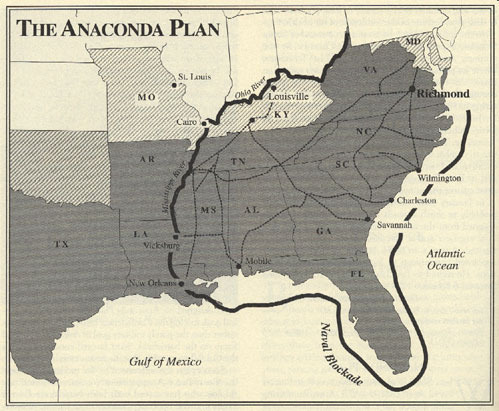
The Union could complete the seize of the economy of the Confederate States as a part of the Anaconda Plan if Vicksburg was captured.
The capture of Vicksburg would also divide the Confederate States which would viciously weaken the power of the Confederacy.
Jefferson Davis and Abraham Lincoln both knew the importance of Vicksburg. Ulysses S. Grant and the Army of the Tennessee drove John C. Pemberton’s Confederate Army of Mississippi to Vicksburg.
in the middle of May 1863 which the Confederate forces resisted but surrendered as they couldn’t stand the siege by both the Army of the Tennessee and the Union navy from the river.


As the western theater of the Civil War became crucial, Lincoln promoted Ulysses S. Grant the commander of the newly formed Military Division of the Mississippi that combined all forces in the Mississippi region and later on he promoted Grant the General of the Army of the United States.
William Tecumseh Sherman becomes the next commander of the Military Division of the Mississippi. William Tecumseh Sherman leaves a reserve force to defend his supplies while he starts the so called ‘Sherman’s March to the Sea’.
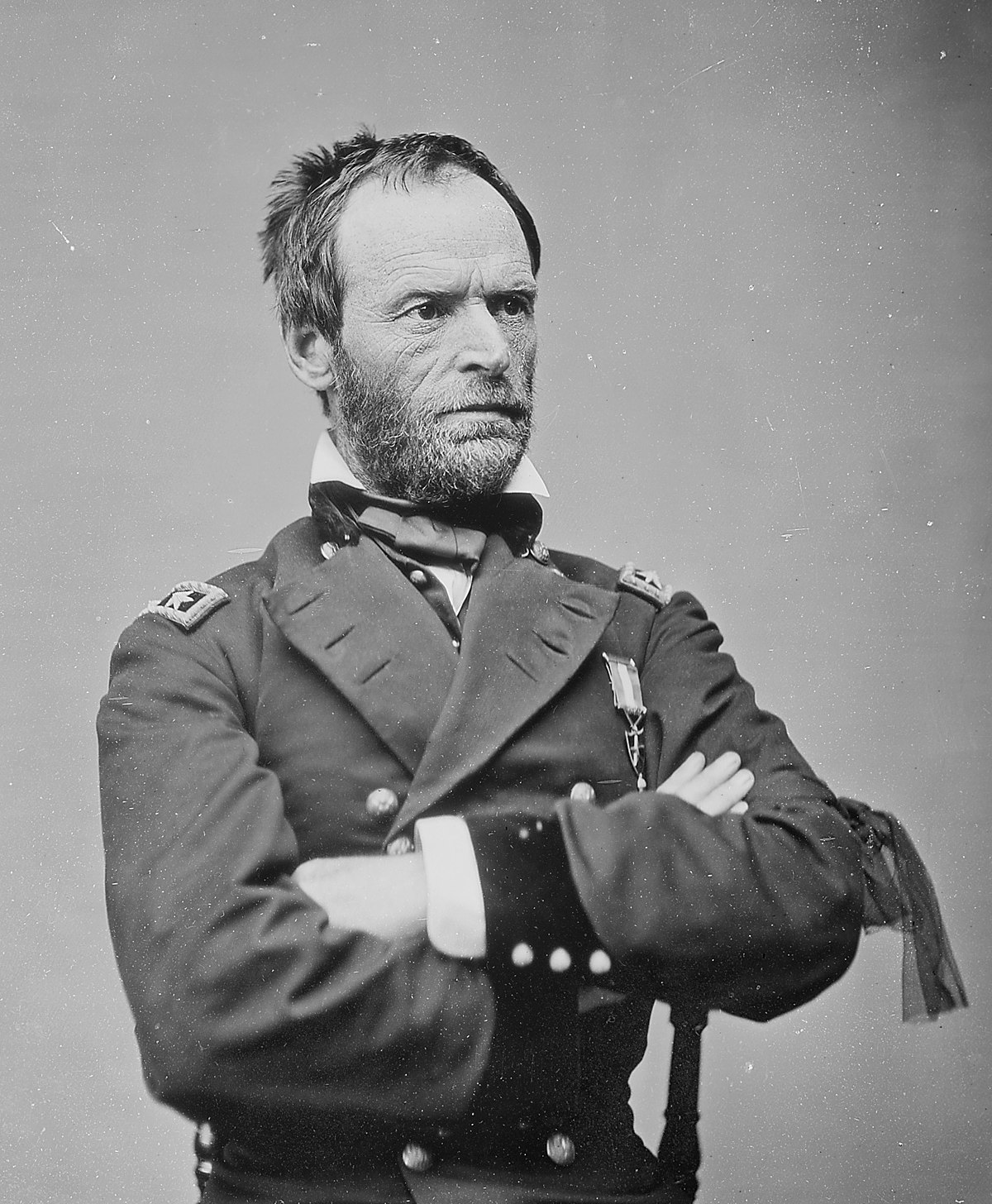

Throughout Georgia, William Sherman performs scorched earth tactics which destroyed railroads, factories, plantations, civilian properties and infrastructure while he drove deeply into enemy territory.
His forces burned down Atlanta and would reach the city of Savannah and the Atlantic Ocean.

Sherman’s March to the Sea torn the economy of Georgia and the Confederate States of the United States.
It wrecked about 300 miles (about 480 km) of railroads, 9.5 million pounds (4,5000 tons of corn) and numerous properties that would affect the economy of the Southern part of the United States of America for tens of years.


● End of the Civil War
After Ulysses Grant became General of the Unites States Army, led the Overland Campaign also known as the Wilderness Campaign which sieged Richmond and Petersburg that was south of Richmond.
As William Tecumseh Sherman’s forces reached Savannah after Sherman’s March to the Sea Sherman’s forces push through South Carolina and North Carolina and heads for Petersburg and Richmond to join Grant’s forces.

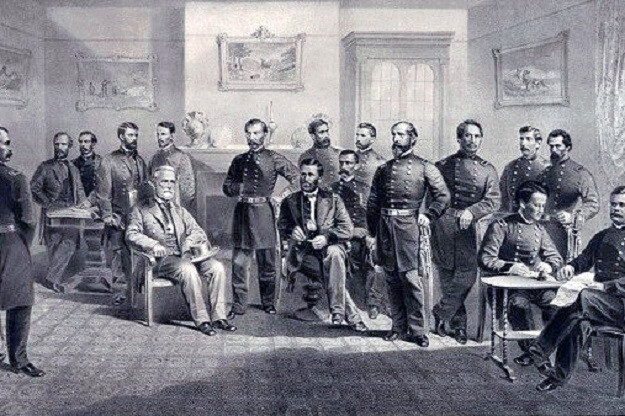
Richmond fell on the 3rd of April 1865 and on the 9th of April 1865, Robert E . Lee who was then the General in Chief of the Armies of the Confederate States surrendered to Ulysses Grant at the Battle of Appomattox Court House.


Jefferson Davis would be imprisoned on 22nd May 1865, and released on 13 Mary 1867. He would be under indictment until Andrew Johnson’s granting amnesty and pardon to all participants in the rebellion in 1868(This was the second).
Robert E. Lee wasn’t imprisoned but he was rejected on the first Proclamation of Amnesty and Pardon o persons who had participated in the rebellion against the United States and admitted on the second amnesty in 1868.


● Assassination of Abraham Lincoln
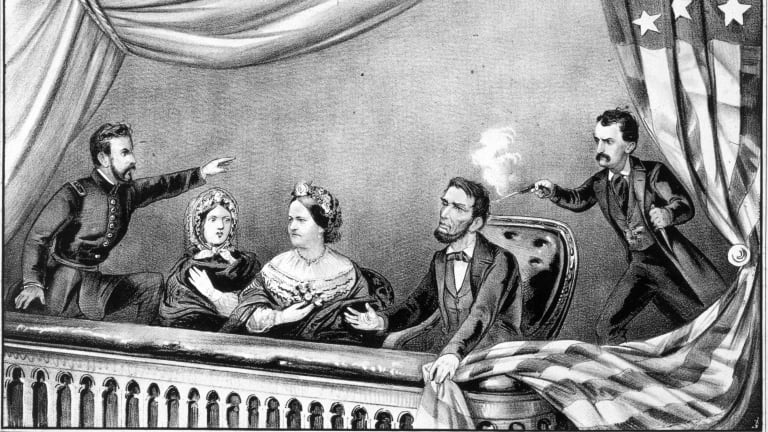
Before Abraham Lincoln could prepare to embrace the Confederate States of America, he was died in the morning of 15th April 1865.
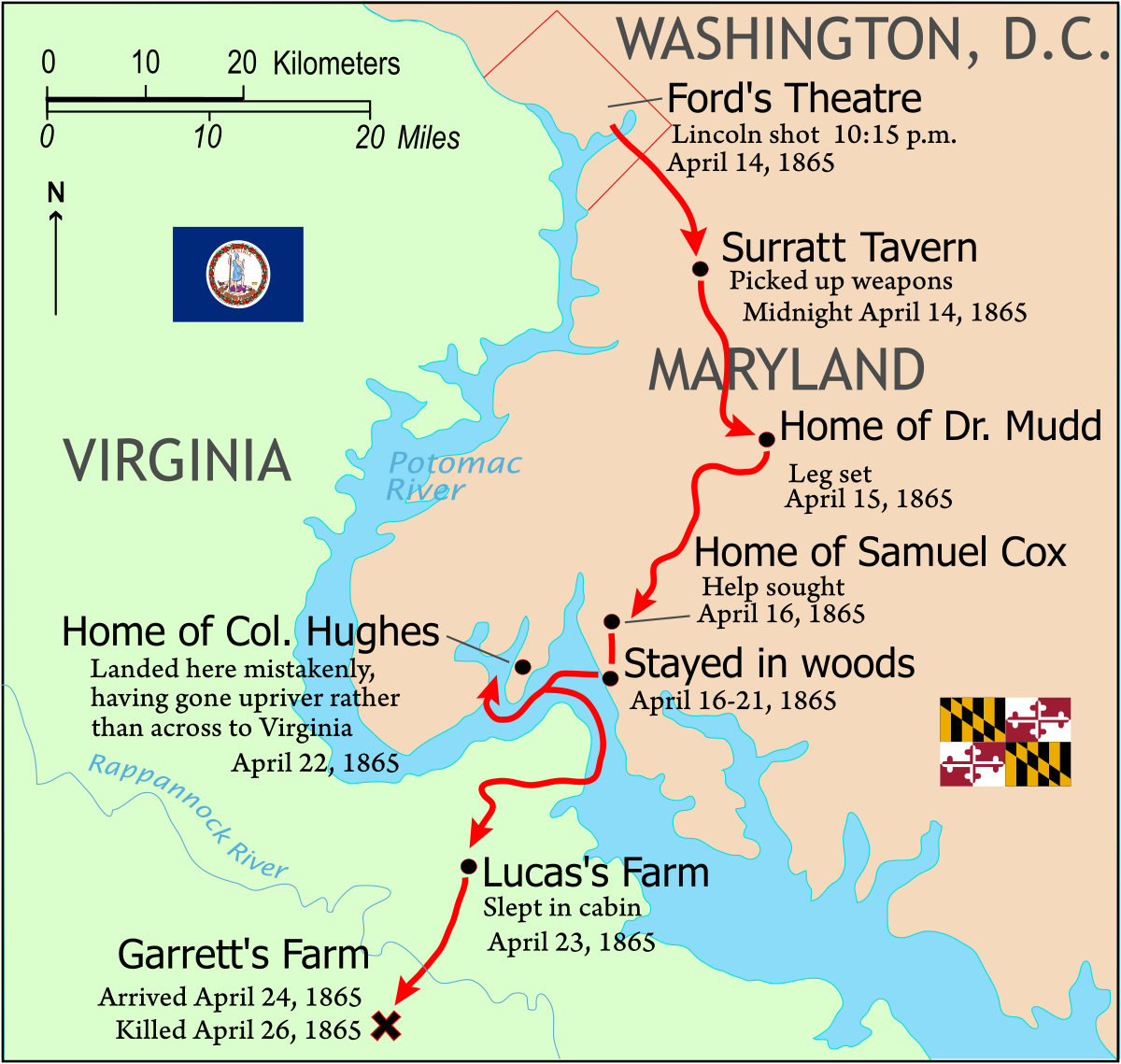
On 14th April 1865, Abraham Lincoln was enjoying the comedy Our American Cousin at Ford’s Theater. However, a radical Confederate supporter and actor John Wilkes Booth shot a single shot in the back of Lincoln with a derringer.



John Wilkes Booth knew John T. Ford who was the owner of Ford’s theater and had free access around the theater as he frequently performed there.
John Wilkes Booth managed to escape to Virginia where he was shot while resisting to federal troops trying to arrest him at Garrett’s Farm close to Fredericksburg.
Although Abraham Lincoln passed away in a tragedy, what he did in life echoes in an eternity.

'International & History' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [USA] - 미국 12대 대통령 재커리 테일러 미국 13대 대통령 밀러드 필모어 (0) | 2023.03.08 |
|---|---|
| [USA] - 미국 11대 대통령 제임스 녹스 폴크 (0) | 2023.03.07 |
| [USA] - 16th President of the USA Abraham Lincoln feat. American Civil War - Part 1 (0) | 2023.03.07 |
| [USA] - 미국 9대 대통령 윌리엄 헨리 해리슨 미국 10대 대통령 존 타일러 (0) | 2023.03.07 |
| [USA] - 15th President of the USA James Buchanan (0) | 2023.03.07 |



