Defrosting methods of tuna at Home and Why are tunas kept in very cold environments lower than -60°C
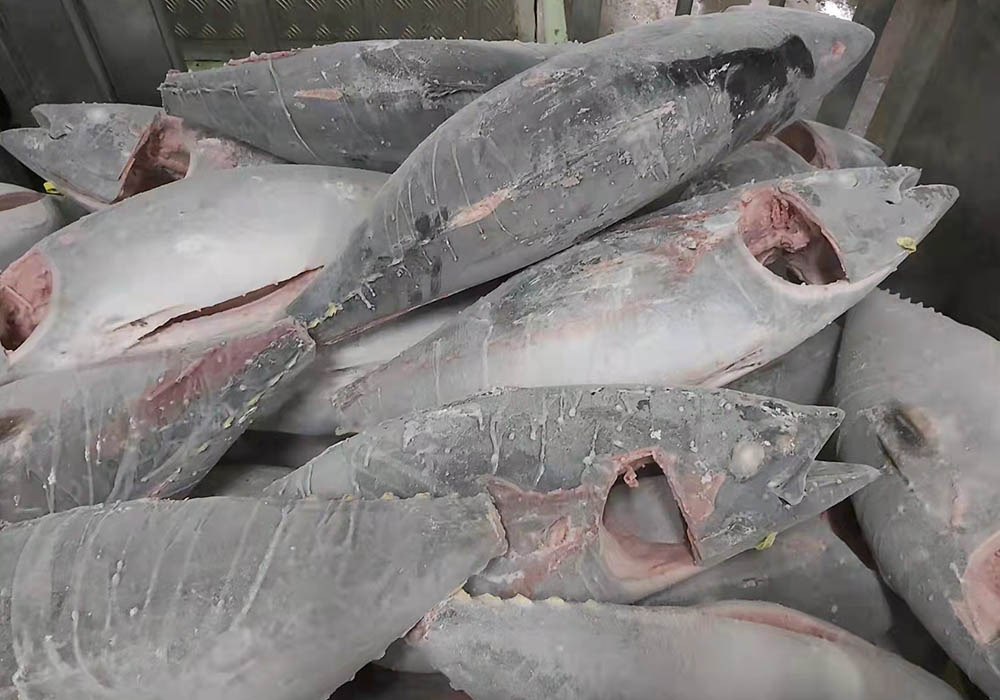

Tuna freezers are different from household freezers
Commercial tuna freezers freeze tuna at least -60°C that is -76 °F. Ordinary household freezers are however only go down to maximum -18°C that is about 0 °F.
Thus, the moment a frozen block of tuna starts shipping, the tuna block is already defrosting dand even if stored in a household freezer, it is technically defrosting and melting in your freezer.
Thus, frozen tuna blocks should be consumed within at least a week upon receival and long storage even in the freezer would harm the quality of the tuna.




Why do tuna have to freeze in such low temperatures
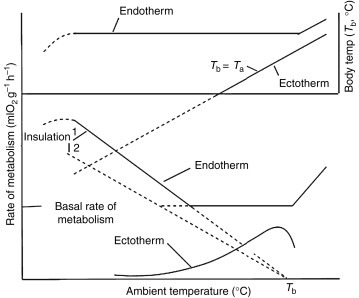
Fishermen and merchants describe that ‘tuna meat’ temperature is a ‘hot meat’ and it would start to ‘melt’ if not frozen at -60°C. This is actually a good description of the tuna meat. Tuna as explained in another post are endothermic also known as homeothermic and warmblooded.
The point is endothermic animals maintain a certain temperature and has a high metabolic rate compared. Most fish are ectothermic thus, cold blooded and don’t raise their body temperature.


Tuna and their cells, however when they aren’t completely dormant in such low temperature as -60°C, metabolism of the tuna would increase the temperature of the tuna.
Like humans could survive and struggle to increase their temperature in -18°C, although dead, the tuna cells would also become more active and increase the temperature that accelerate the deterioration of tuna.


Why does the temperature increase make the tuna go bad
Tuna have a high metabolism rate because they need to use energy to create heat to keep their body temperature. Metabolism literally means the chemical activities induced by biological activities of an organism.
The increase of metabolism itself means that much more chemical activities occur in the tuna, thus at so low temperatures like -60°C, the tuna would stay dormant but in temperatures like -18°C, cell metabolism occurs and the chemical reactions as a result quickly makes the tuna go bad.


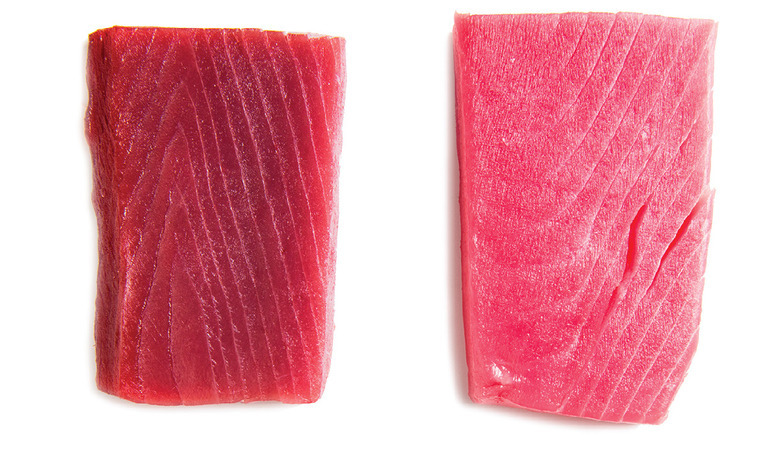
Metabolism frequently involve oxidation-reduction activities and tuna has many components that attract oxygen and has a high reactivity with oxygen such as the high poly unsaturated fats contents and the myoglobin of the meat.
Thus outside -60°C temperature environments, tuna meat quality quickly changes and it requires caution or quick consumption and shipping.
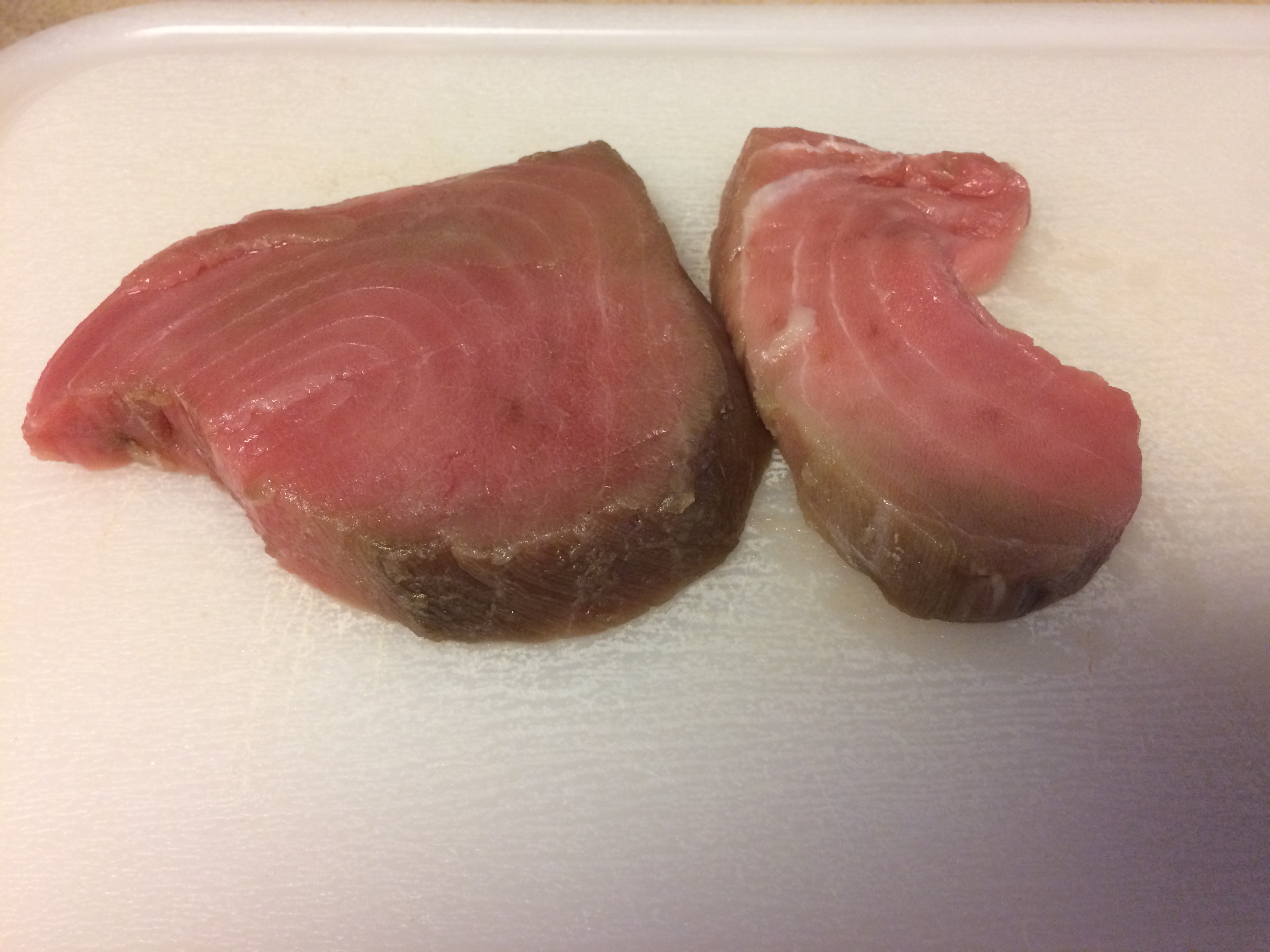




Why proper defrosting is important for tuna
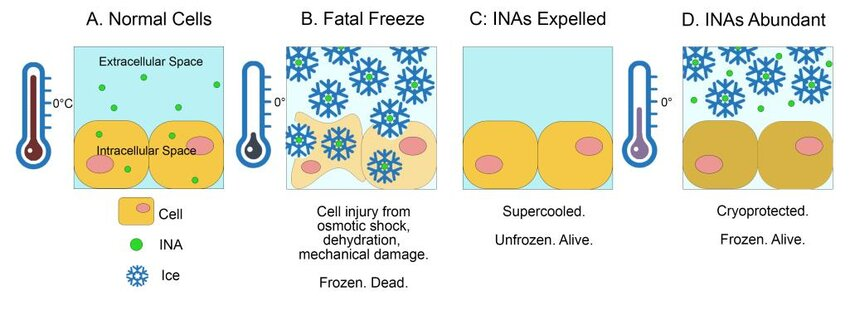
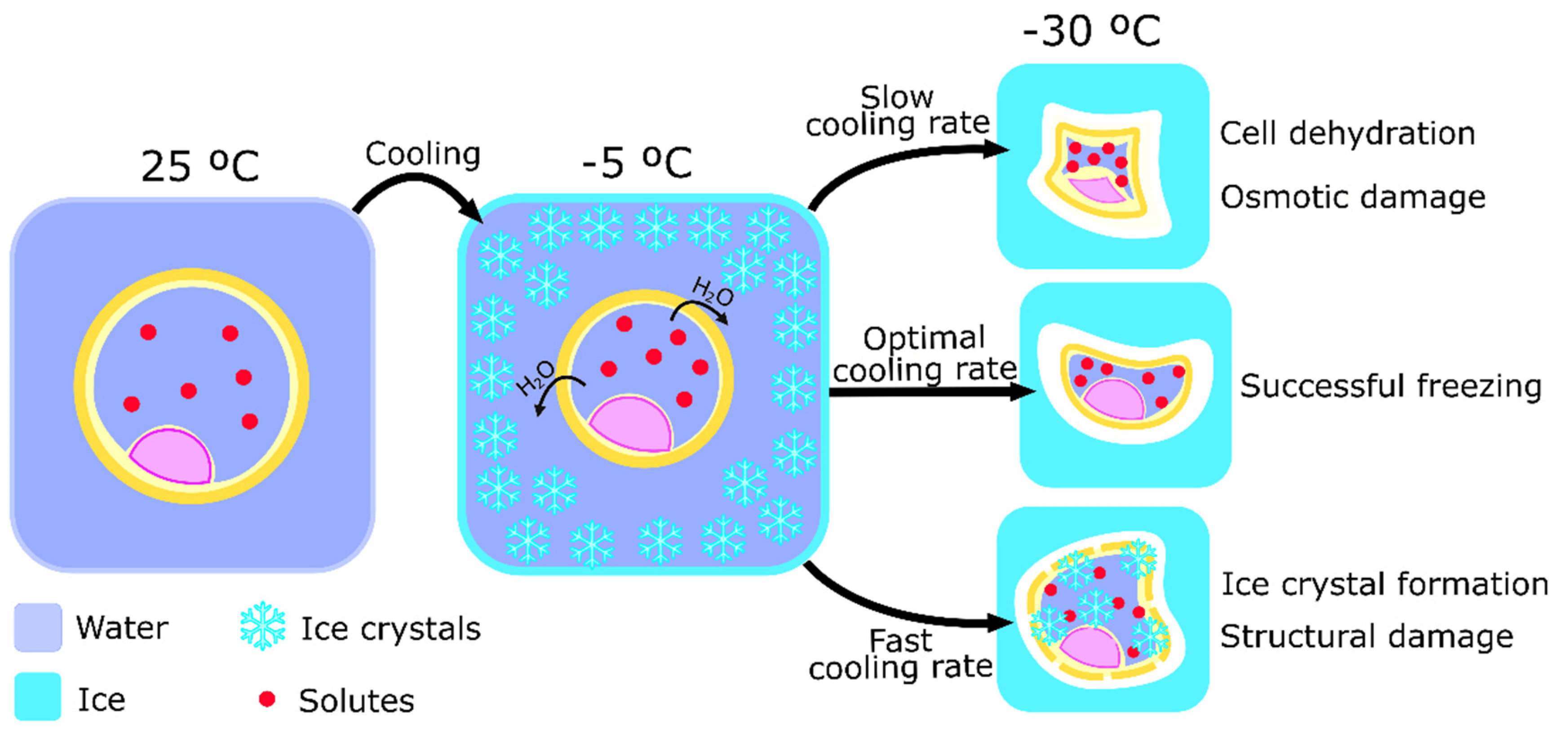
Ice which is the solid form of water is very hard and it forms pointy structures that could pierce through cell membranes and burst the cell cytoplasms in molecular level.
When ice melts to water, ice doesn’t simply change to water and repetitive processes of water-ice recrystalization. Also, water is a special molecule that increases volume when it becomes ice.


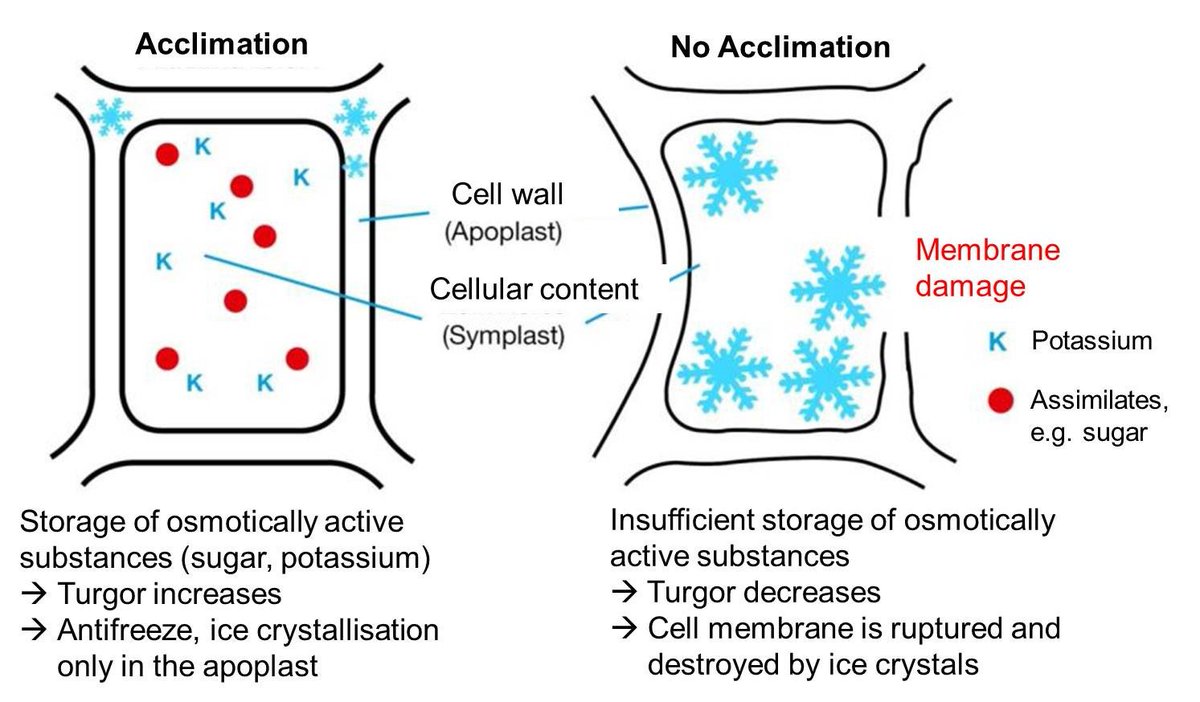

Thus, to minimize the cell damage and keep the quality of the frozen tuna and fish, it is much important to minimize the cell damage that could be induced by repetitive transition of ice-water and the ice’s sharp edges that directly damage the membranes and the expansion caused by the ice-water change.
Even for humans, freezing humans is a technology that could be developed with the technology of 2025. However defrosting humans without damaging the cell membranes is most difficult and presumably impossible to resolve.
Defrosting and the tuna quality relationship
Proper defrosting of tuna is most important to serve tuna as a dish. Tuna that hasn’t been defrosted properly would have severe damage in the cell membranes, thus trigger necrosis and induce the unprogrammed cell death chain reactions of the cells.
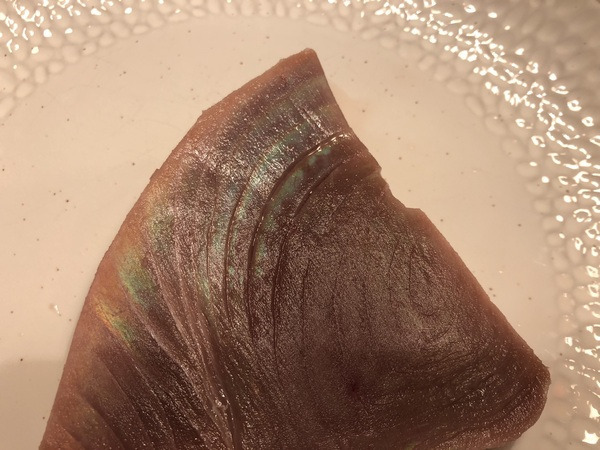


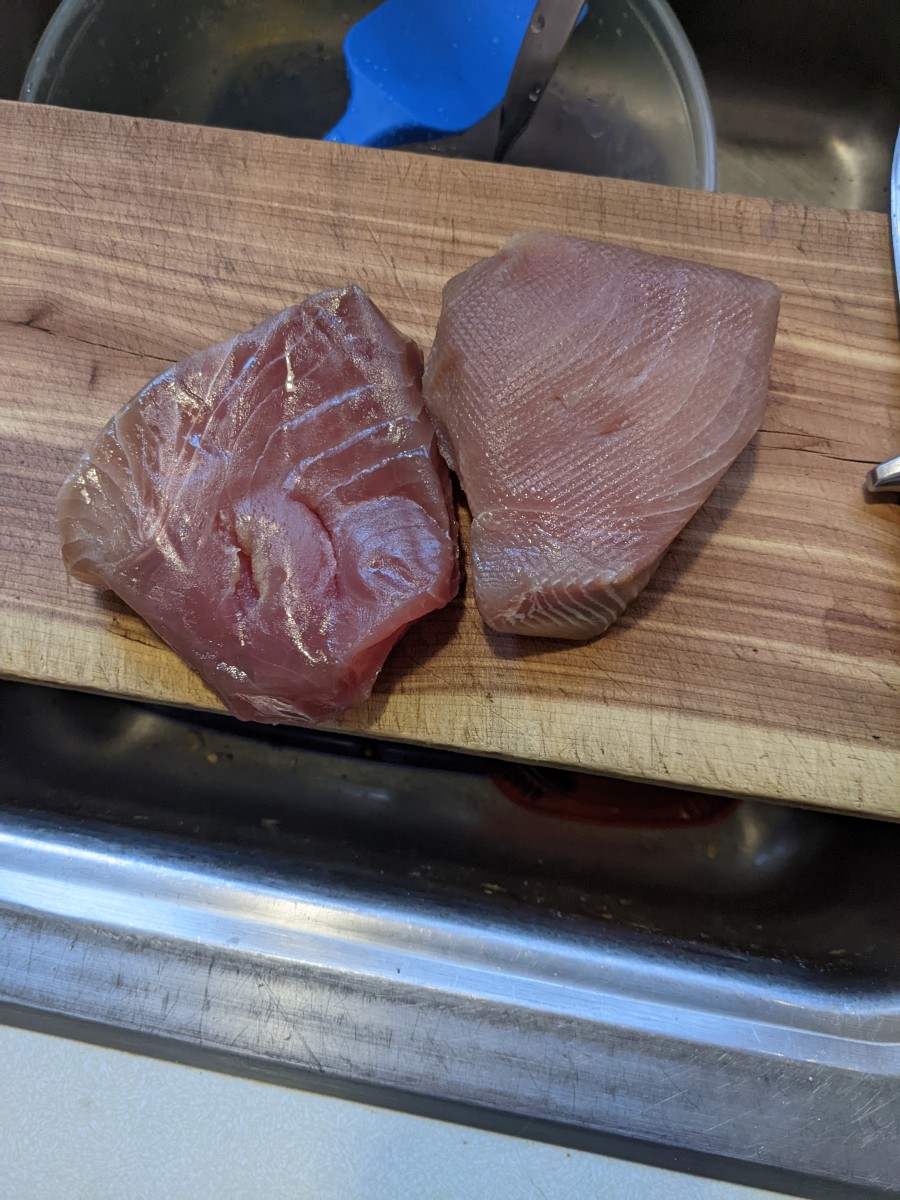
This would quickly harm the quality of the meat and make it inedible. Also, tuna that wasn’t properly defrosted and already faced many damages tend to quickly change color to brown and become inedible in a short amount of time.
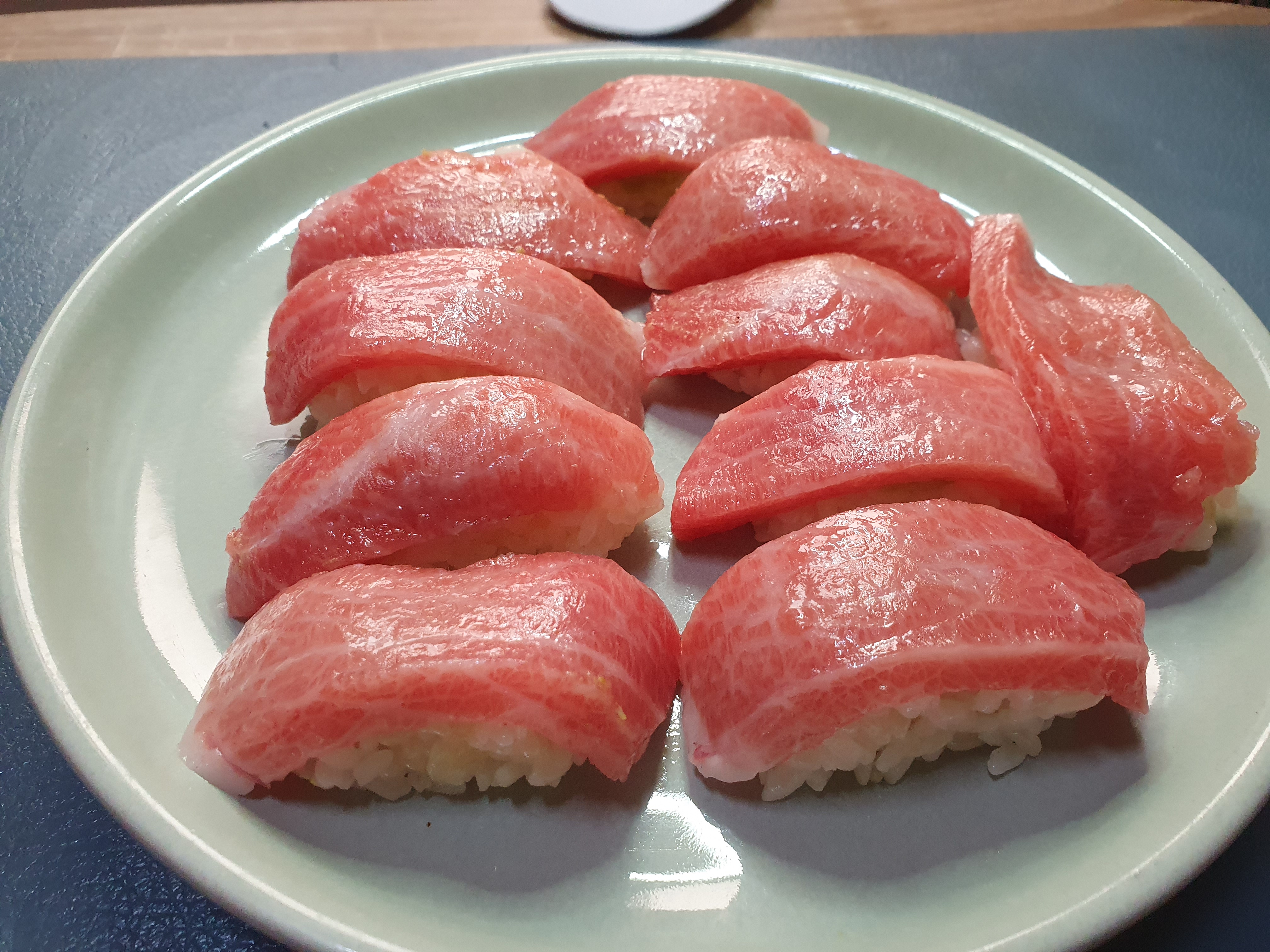
Thus for high quality tuna like the bluefin tuna, defrosting is one of the grand techniques that is difficult to master.
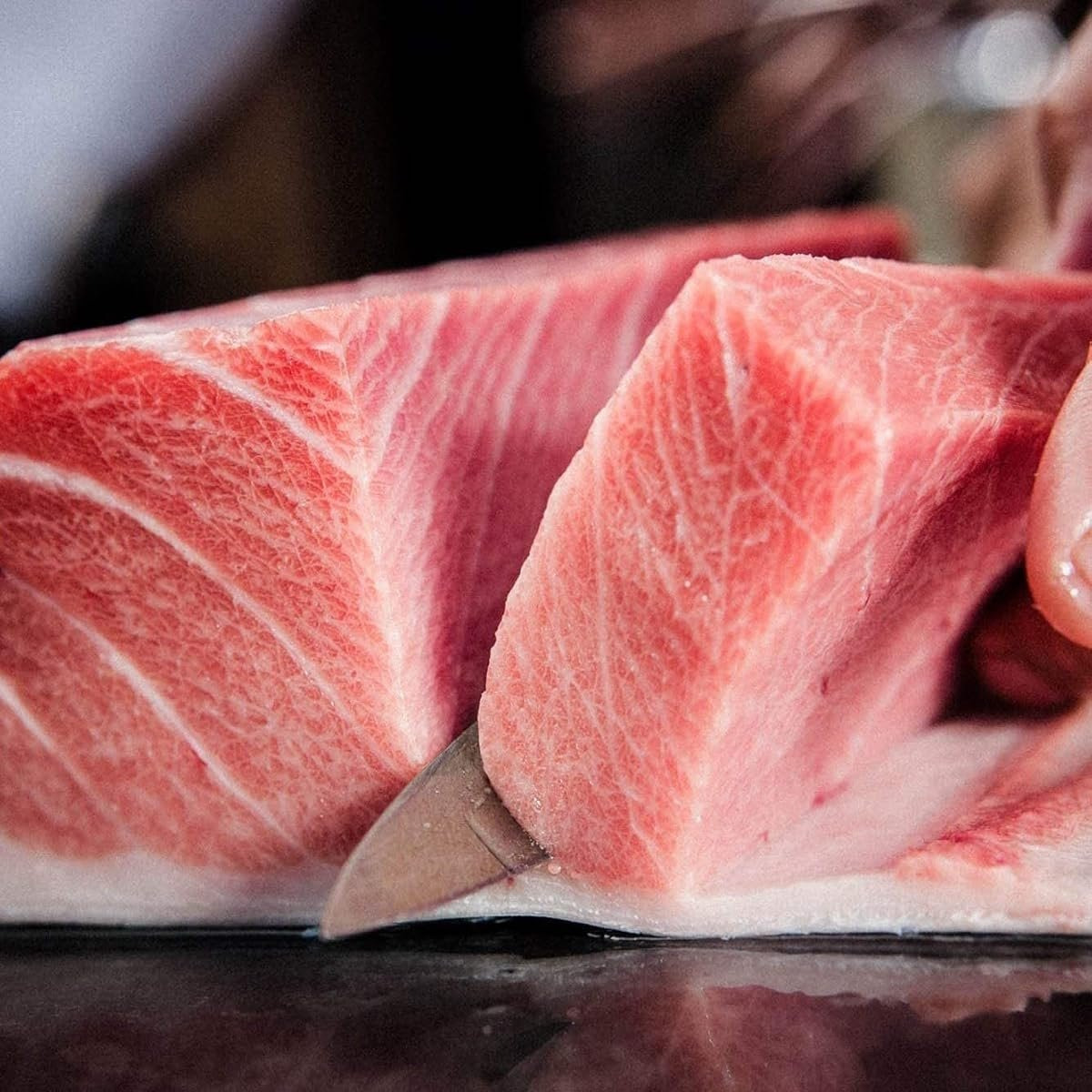


How to defrost tuna the easiest way for sashimi – saltwater defrosting
*Preparation : Thawed paper(this is a specialized paper towel used to remove water from fish.), salt, warm water, frozen tuna block, cold water
Prepare a warm water(lukewarm temperature) that is just about the temperature of a human. Enough water to completely soak the frozen tuna block must be prepared.
Put salt into the prepared water. The salinity of the water should at least be similar to the ocean water. However, a good amount of salt would be sufficient enough if you don’t have a clue.
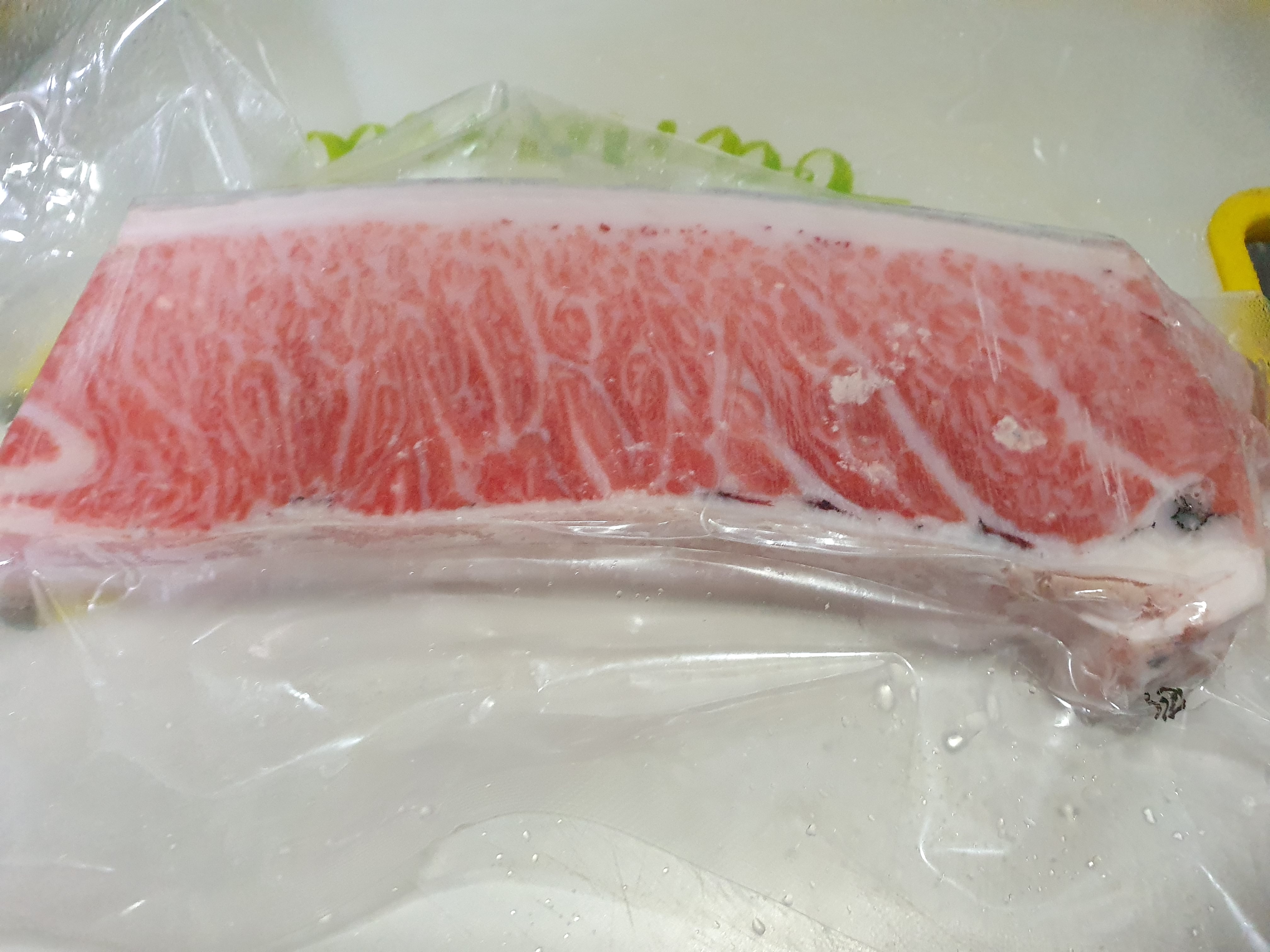
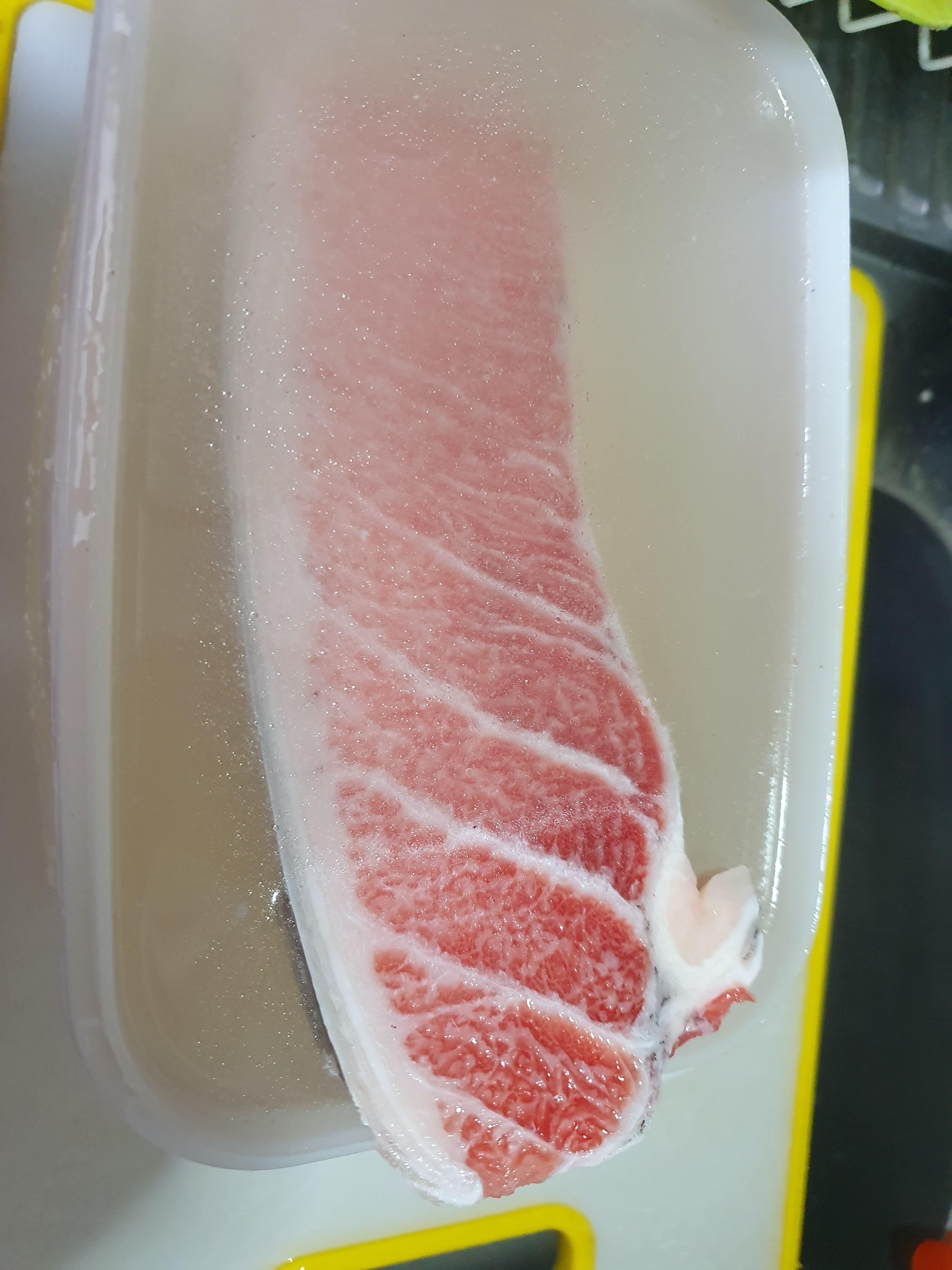


Wash the frozen tuna block in ‘cold’ water that is flowing to wash off any residues on the frozen tuna block. Just turn on the tap water in cold water and wash the frozen tuna block. Once residues are removed, you could finish this process.
Soak the whole frozen tuna block in the prepared warm salt water and place it for 2~3 minutes. For tuna with fatty parts like the Otoro it should take 2 minutes while for leaner Akami, it should take 3 minutes or a bit longer.
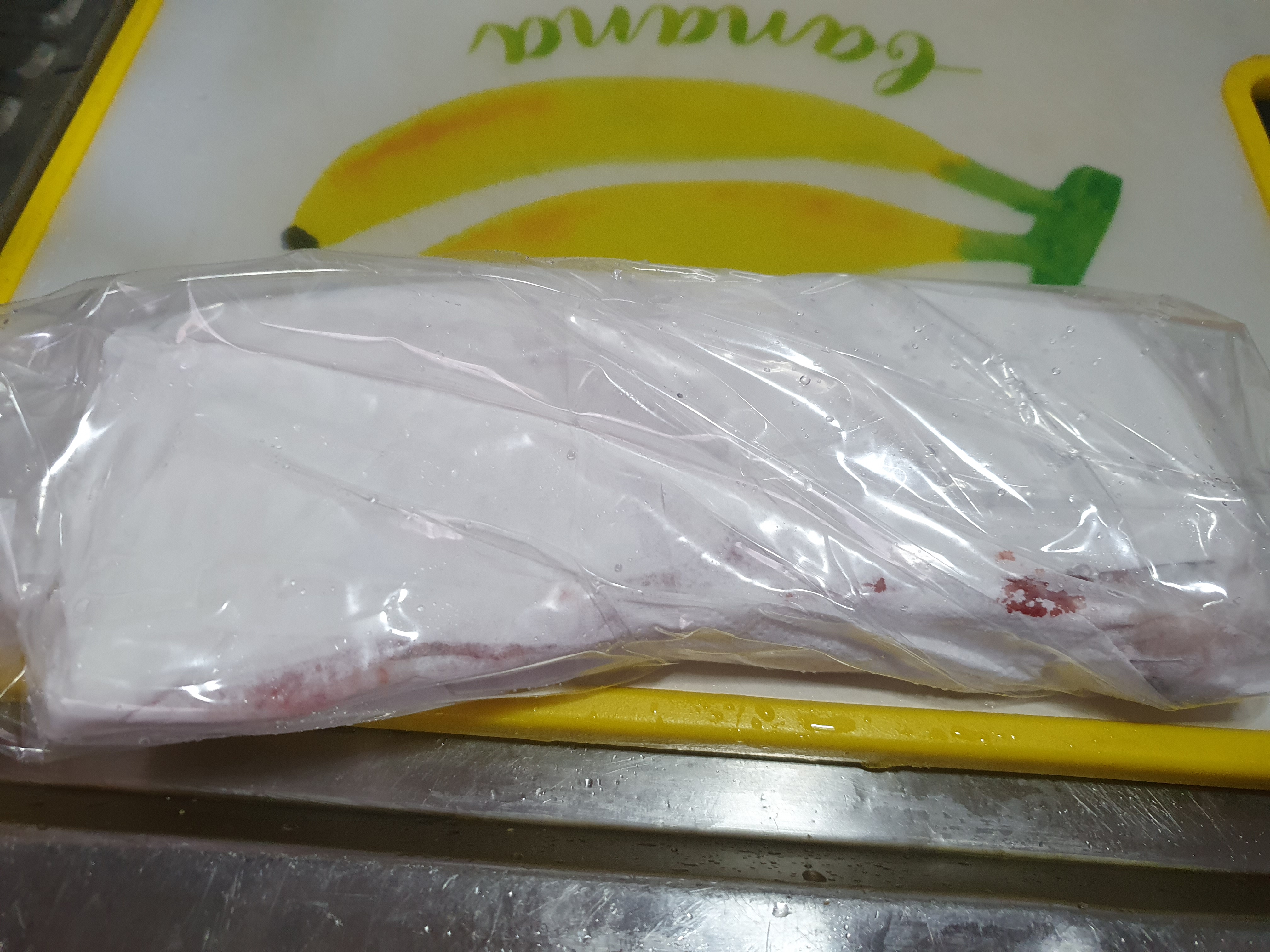


Take the tuna block out from the water and remove all water with Thawed paper. Wrap the tuna block as tight as possible with all the water removed with Thawed paper. If possible vacuum seal the tuna block.
Place the tuna in the refrigerator for 2~4 hours. However, it should be shorter for fatty parts like the Otoro.
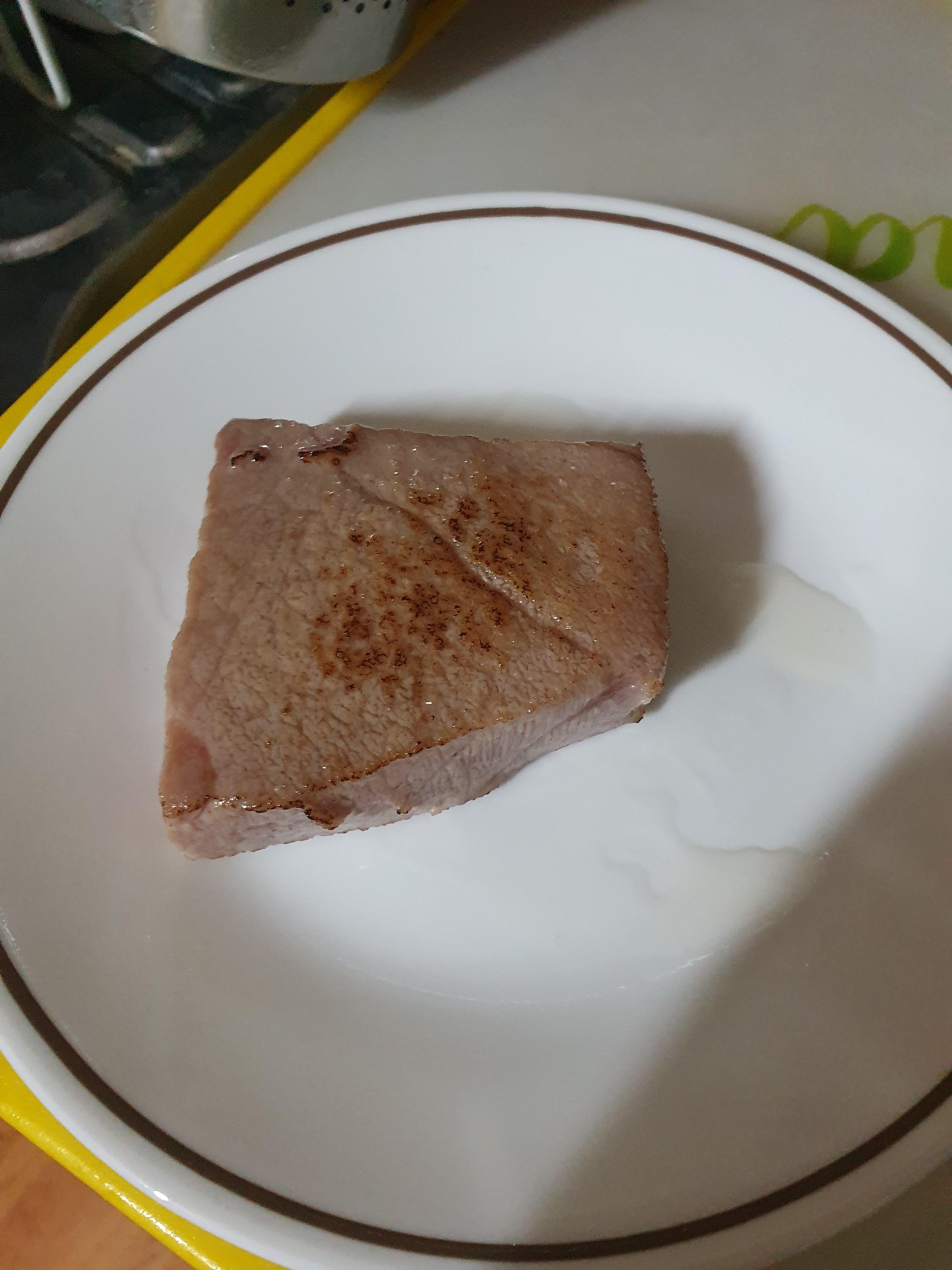
Carefully take out the tuna block and remove the skin on top and the membrane on the bottom of the tuna block.
*Be very cautious as this is the most dangerous part of the process and you could be hurt.
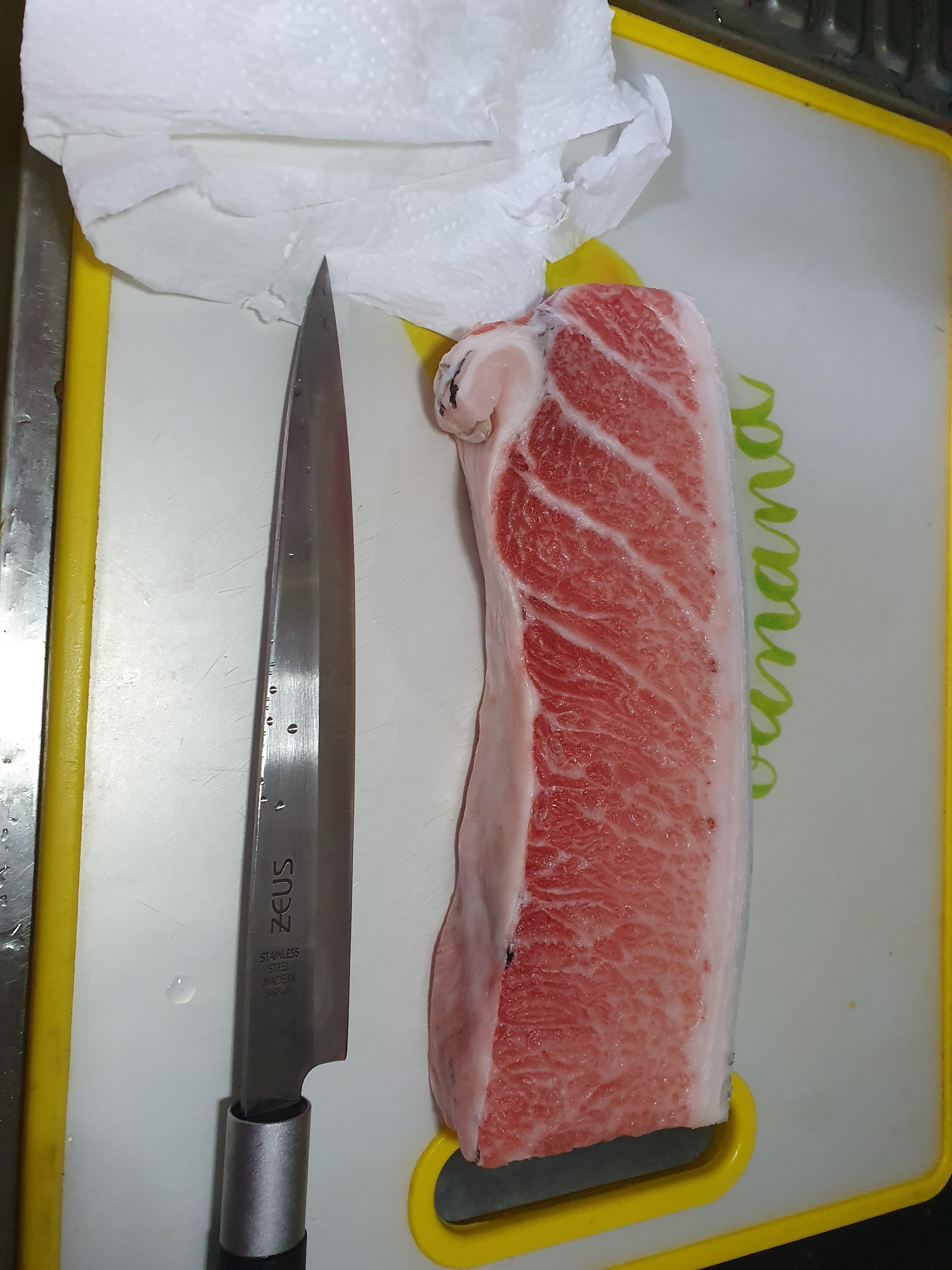


Check for any bone splinters and fragments on the bottom of the tuna block and remove the bones
*Tuna bones could damage your teeth
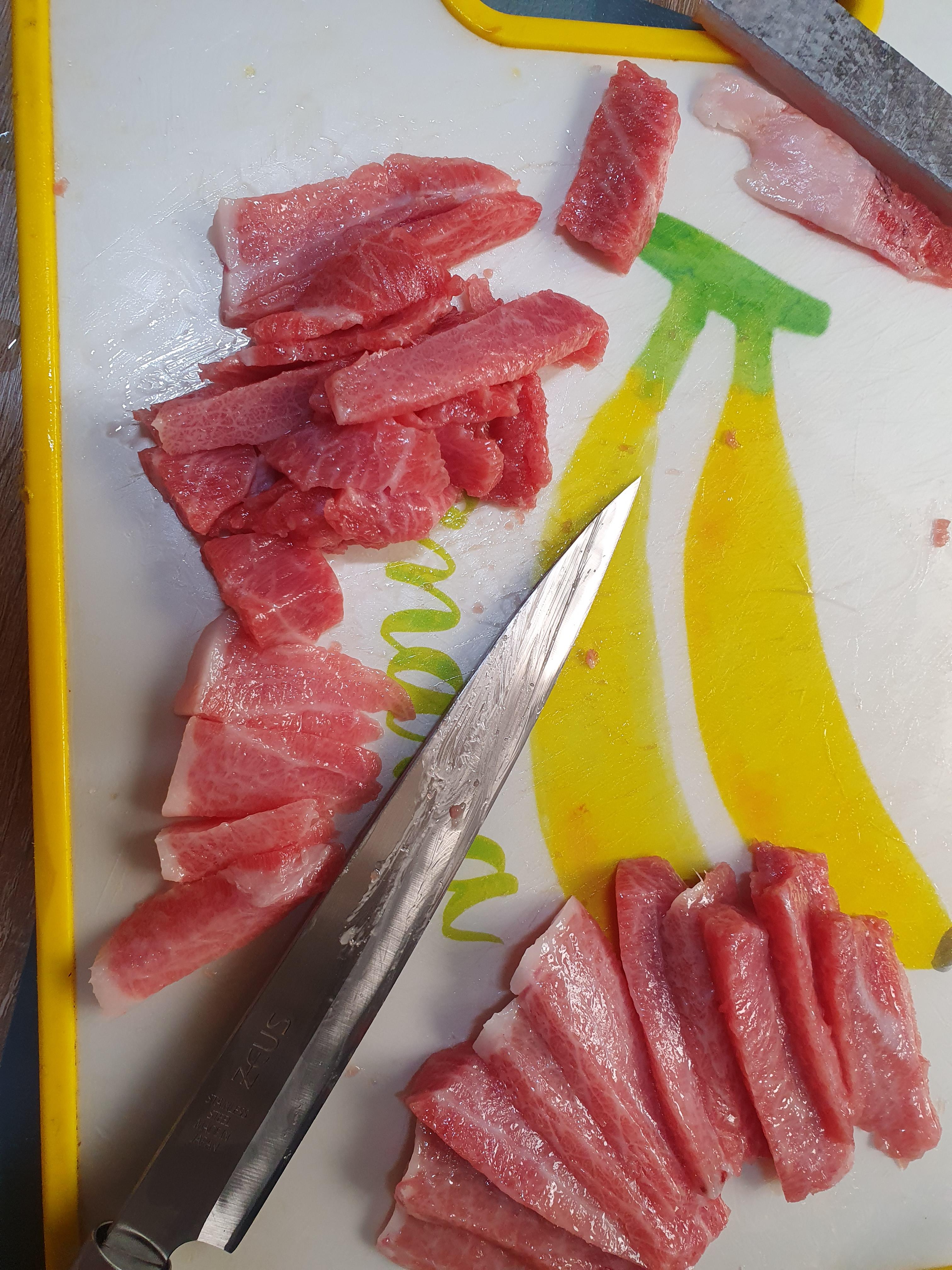
Properly defrosted tuna shouldn’t be tough to slice. Slice the tuna for sushi or sashimi and enjoy.


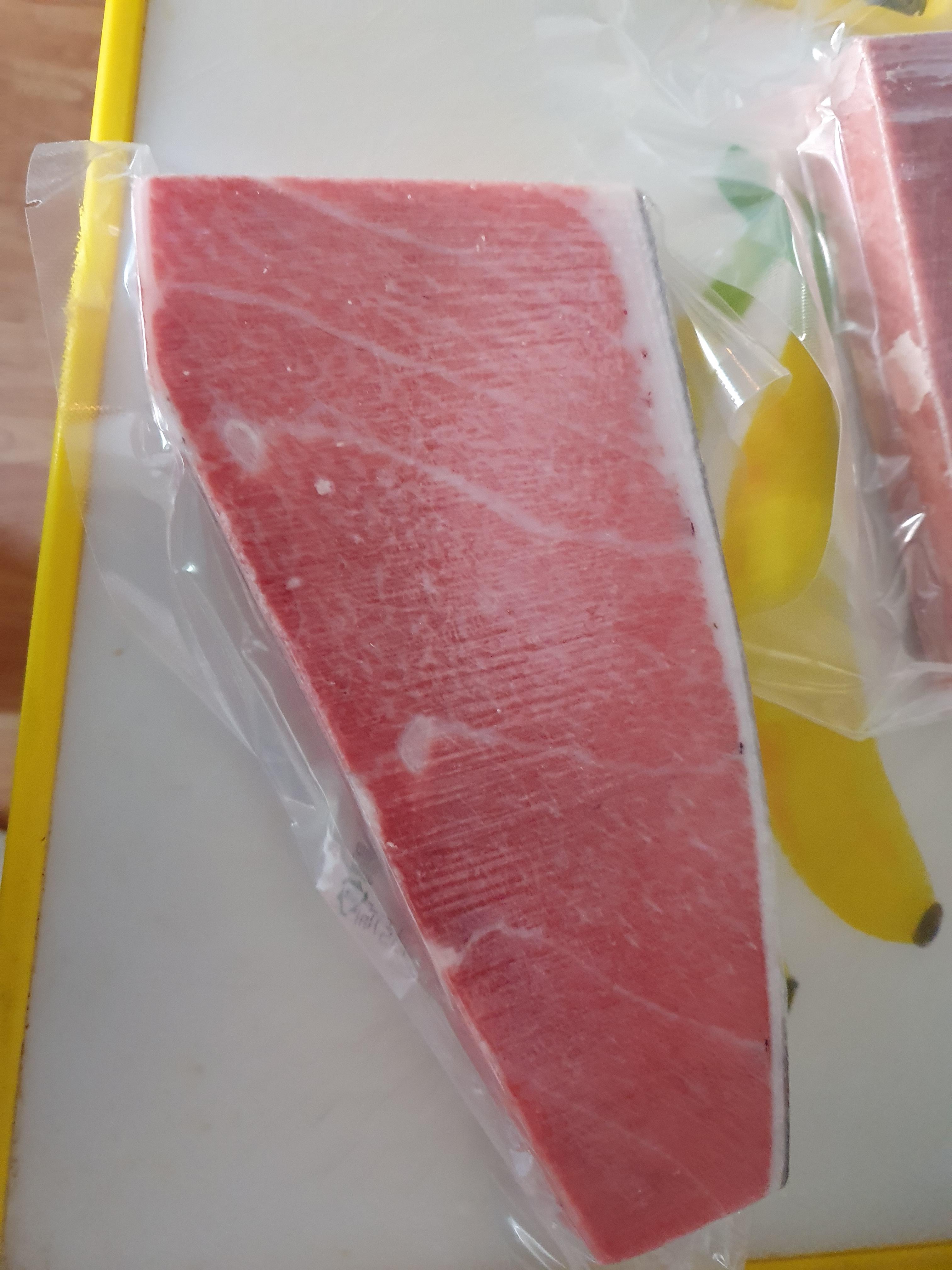
Ice water Defrosting method for frozen tuna
*Never tried this method. It requires a vacuum package
Prepare ice water where the tuna block could completely submerge. >> vacuum seal the tuna in a bag >> Place the vacuum sealed tuna in the ice water for 30~40 minutes >> Ice would from around the bag and this should be removed. Tuna should be checked for every 3~5 minutes >> Remove the tuna from the water and remove the water of the tuna once more >> vacuum seal the tuna after wrapping the tuna with thawed paper>> Enjoy
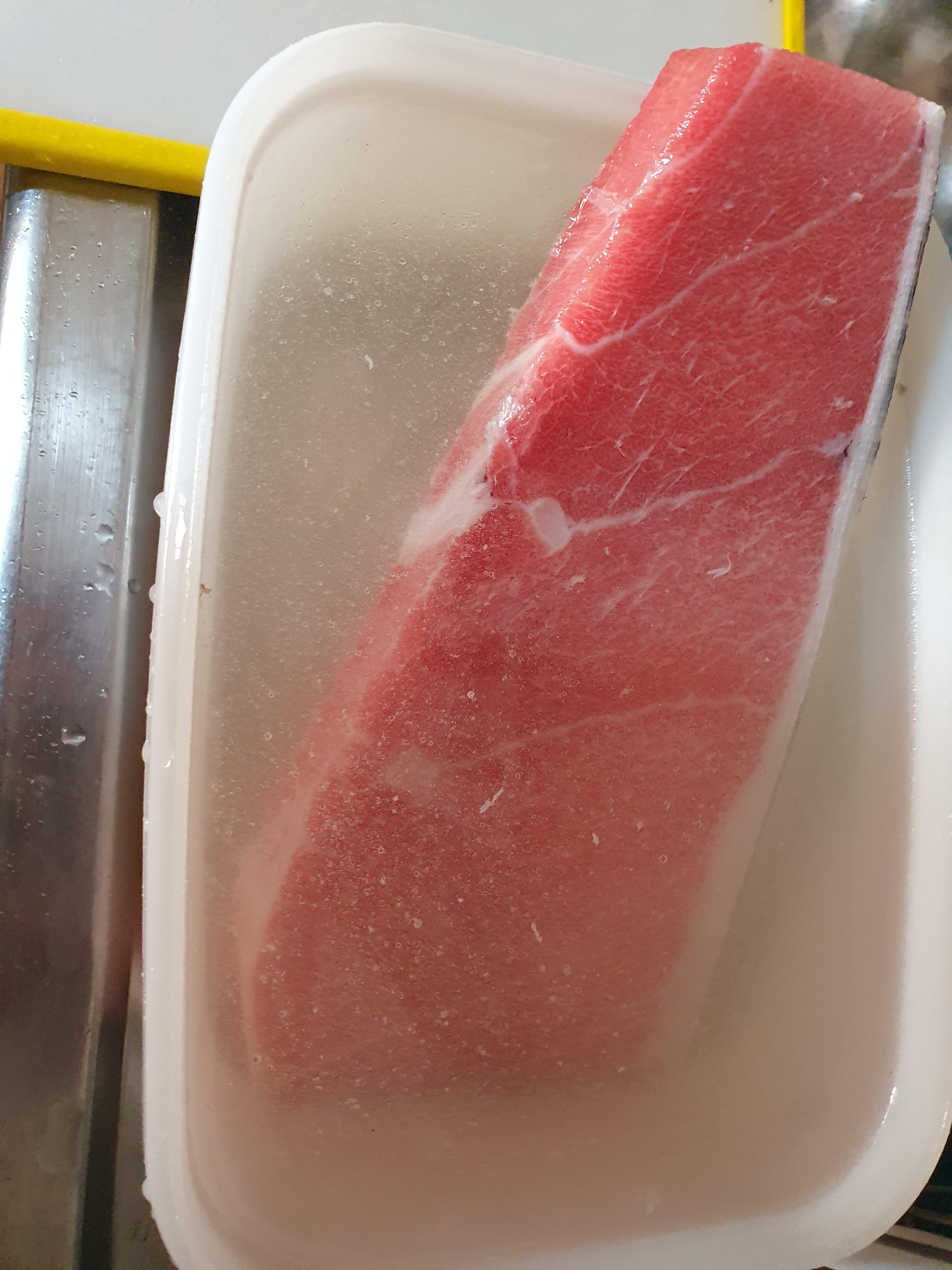




Cold water and vacuum sealing method for frozen tuna
*Never tried this method as well . It requires a vacuum package
Prepare cold water that isn’t frozen but just about 1°C where the tuna block could completely submerge >> Wash the tuna block for 30 seconds in cold water >>> Remove the water of the tuna block with thawing paper >> Vacuum seal the tuna and place it in the prepared cold water >> Put the cold water with the tuna submerged for 2 hours in the refrigerator >> Take out the tuna and remove water >> Rap and seal the tuna from air (vacuum seal) and eat after 2~6 hours.




